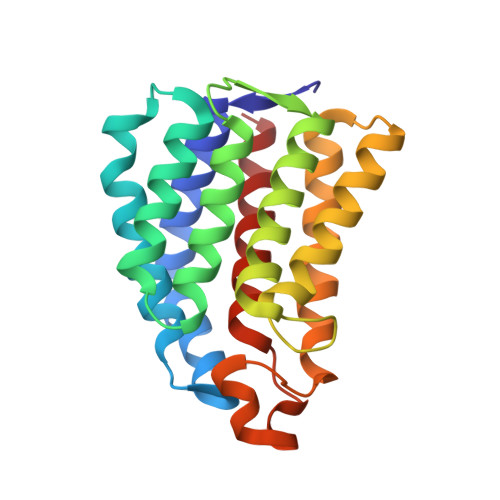
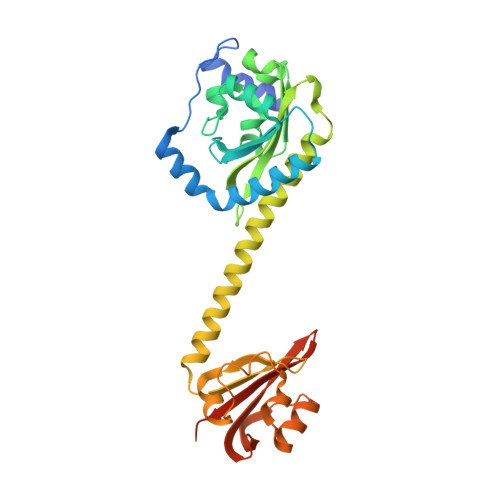
Coiled-Coil Helix Rotation Selects Repressing or Activating State of Transcriptional Regulator DhaR.
Shi, R., McDonald, L., Cygler, M., Ekiel, I.(2014) Structure 22: 478-487
- PubMed: 24440518
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.11.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LRX, 4LRY, 4LRZ - PubMed Abstract:
Escherichia coli dihydroxyacetone (Dha) kinase consists of two subunits, DhaK and DhaL. Transcription of dha operon is regulated by the DhaR transcription factor and its action is under control of the kinase subunits. DhaR is activated by interaction with DhaL while it is repressed by DhaK. We have determined the structures of DhaK and DhaL bound to the tandem GAF-like and PAS domains of the DhaR, providing an architectural model for how GAF/PAS tandem domains work together in binding protein partners. The structures reveal a mechanism of opposite transcriptional regulation by the DhaK and DhaL subunits. The kinase subunits interface with DhaR through surfaces that partially overlap with their active sites, allowing sensing of ATP- versus ADP-loaded DhaL subunit and also precluding a ternary complex between DhaK-DhaL and DhaR. The rotation of helices within the DhaR coiled-coil linker upon DhaL binding provides the mechanism for transmitting the binding signal from the GAF/PAS domains to the C-terminal DNA-binding domain.
- Département de Biochimie, de Microbiologie et de Bio-informatique, PROTEO, Université Laval, Pavillon Charles-Eugene-Marchand, Québec City, QC G1V 0A6, Canada; Institut de Biologie Intégrative et des Systèmes (IBIS), Université Laval, Pavillon Charles-Eugene-Marchand, Québec City, QC G1V 0A6, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: