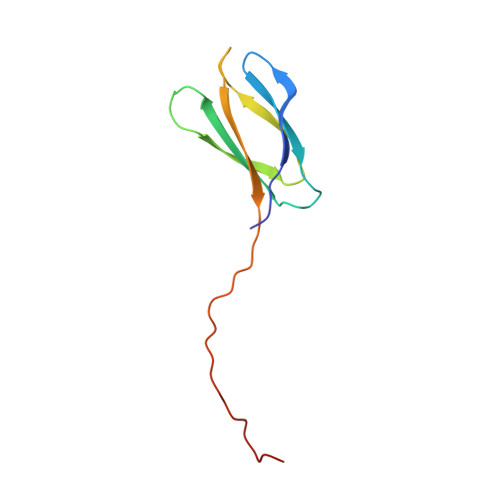
C-terminal beta-strand swapping in a consensus-derived fibronectin Type III scaffold.
Teplyakov, A., Obmolova, G., Malia, T.J., Luo, J., Jacobs, S.A., Chan, W., Domingo, D., Baker, A., O'Neil, K.T., Gilliland, G.L.(2014) Proteins 82: 1359-1369
- PubMed: 24375666
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24502
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LPT, 4LPU, 4LPV, 4LPW, 4LPX, 4LPY - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structures of six different fibronectin Type III consensus-derived Tencon domains, whose solution properties exhibit no, to various degrees of, aggregation according to SEC, have been determined. The structures of the five variants showing aggregation reveal 3D domain swapped dimers. In all five cases, the swapping involves the C-terminal β-strand resulting in the formation of Tencon dimers in which the target-binding surface is blocked. All of the variants differ in sequence in the FG loop, which is the hinge loop in the β-strand-swapped dimers. The six tencon variants have between 0 and 5 residues inserted between positions 77 and 78 in the FG loop. Analysis of the structures suggests that a non-glycine residue at position 77 and insertions of <4 residues may destabilize the β-turn in the FG loop promoting β-strand swapping. Swapped dimers with an odd number of inserted residues may be less stable, particularly if they contain proline residues, because they cannot form perfect β-bridges in the FG regions that link the swapped dimers. The Tencon β-swapped variants with the longest FG sequences are observed to form higher order hexameric or helical oligomeric structures in the crystal correlating well with the aggregation properties of these domains observed in solution. Understanding the structural basis for domain-swapped dimerization and oligomerization will support engineering efforts of the Tencon domain to produce variants with desired biophysical properties.
- Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Biotechnology Center of Excellence, 1400 McKean Road, Spring House, Pennsylvania, 19477.
Organizational Affiliation: