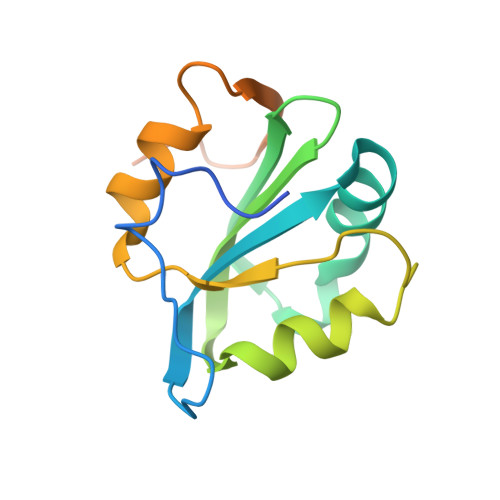
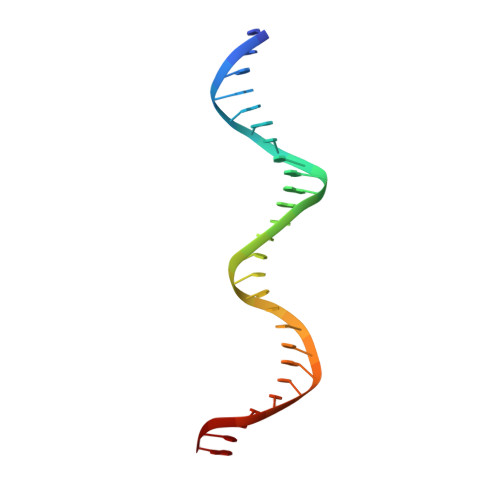
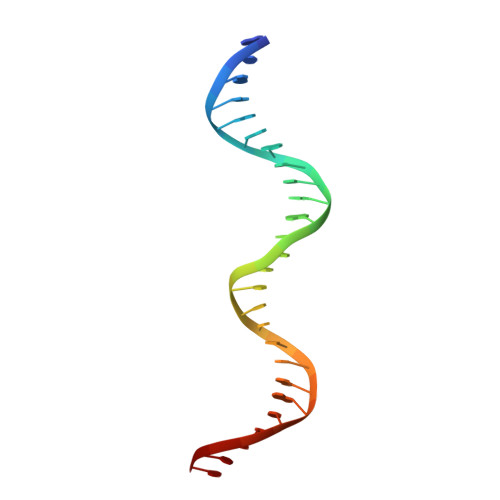
Polyomavirus large T antigen binds symmetrical repeats at the viral origin in an asymmetrical manner.
Harrison, C., Jiang, T., Banerjee, P., Meinke, G., D'Abramo, C.M., Schaffhausen, B., Bohm, A.(2013) J Virol 87: 13751-13759
- PubMed: 24109229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01740-13
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FB3 - PubMed Abstract:
Polyomaviruses have repeating sequences at their origins of replication that bind the origin-binding domain of virus-encoded large T antigen. In murine polyomavirus, the central region of the origin contains four copies (P1 to P4) of the sequence G(A/G)GGC. They are arranged as a pair of inverted repeats with a 2-bp overlap between the repeats at the center. In contrast to simian virus 40 (SV40), where the repeats are nonoverlapping and all four repeats can be simultaneously occupied, the crystal structure of the four central murine polyomavirus sequence repeats in complex with the polyomavirus origin-binding domain reveals that only three of the four repeats (P1, P2, and P4) are occupied. Isothermal titration calorimetry confirms that the stoichiometry is the same in solution as in the crystal structure. Consistent with these results, mutation of the third repeat has little effect on DNA replication in vivo. Thus, the apparent 2-fold symmetry within the DNA repeats is not carried over to the protein-DNA complex. Flanking sequences, such as the AT-rich region, are known to be important for DNA replication. When the orientation of the central region was reversed with respect to these flanking regions, the origin was still able to replicate and the P3 sequence (now located at the P2 position with respect to the flanking regions) was again dispensable. This highlights the critical importance of the precise sequence of the region containing the pentamers in replication.
- Department of Biochemistry, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: