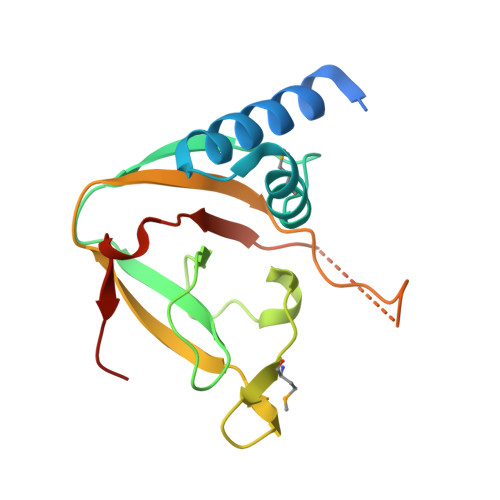
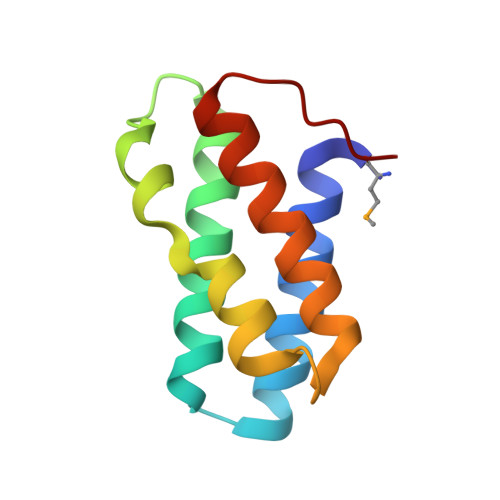
An Interbacterial NAD(P)(+) Glycohydrolase Toxin Requires Elongation Factor Tu for Delivery to Target Cells.
Whitney, J.C., Quentin, D., Sawai, S., LeRoux, M., Harding, B.N., Ledvina, H.E., Tran, B.Q., Robinson, H., Goo, Y.A., Goodlett, D.R., Raunser, S., Mougous, J.D.(2015) Cell 163: 607-619
- PubMed: 26456113
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.027
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ZUY, 4ZV0, 4ZV4 - PubMed Abstract:
Type VI secretion (T6S) influences the composition of microbial communities by catalyzing the delivery of toxins between adjacent bacterial cells. Here, we demonstrate that a T6S integral membrane toxin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Tse6, acts on target cells by degrading the universally essential dinucleotides NAD(+) and NADP(+). Structural analyses of Tse6 show that it resembles mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase proteins, such as diphtheria toxin, with the exception of a unique loop that both excludes proteinaceous ADP-ribose acceptors and contributes to hydrolysis. We find that entry of Tse6 into target cells requires its binding to an essential housekeeping protein, translation elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). These proteins participate in a larger assembly that additionally directs toxin export and provides chaperone activity. Visualization of this complex by electron microscopy defines the architecture of a toxin-loaded T6S apparatus and provides mechanistic insight into intercellular membrane protein delivery between bacteria.
- Department of Microbiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: