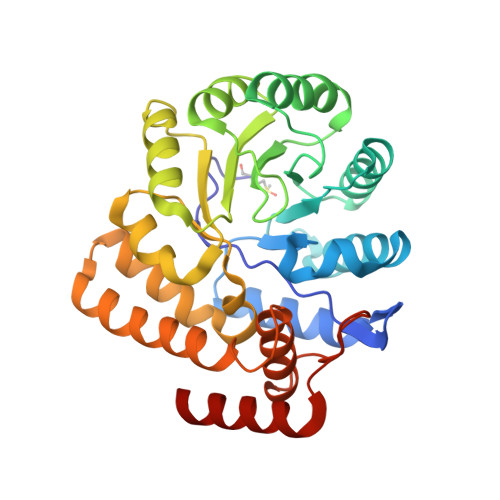
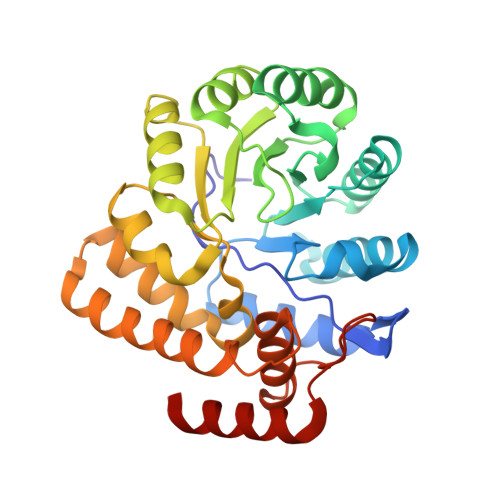
Structure of dihydrodipicolinate synthase from the commensal bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron at 2.1 angstrom resolution.
Mank, N., Arnette, A., Klapper, V., Offermann, L., Chruszcz, M.(2015) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 71: 449-454
- PubMed: 25849508
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X15004628
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XKY - PubMed Abstract:
Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DapA) catalyzes the first committed step of the diaminopimelate biosynthetic pathway of lysine. It has been shown to be an essential enzyme in many bacteria and has been the subject of research to generate novel antibiotics. However, this pathway is present in both pathogenic and commensal bacteria, and antibiotics targeting DapA may interfere with normal gut colonization. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is a Gram-negative commensal bacterium that makes up a large proportion of the normal microbiota of the human gut. The structure of DapA from B. thetaiotaomicron (BtDapA) has been determined. This structure will help to guide the generation of selectively active antibiotic compounds targeting DapA.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of South Carolina, JM Palms Center for Graduate Science Research, 631 Sumter Street, Columbia, SC 29208, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: