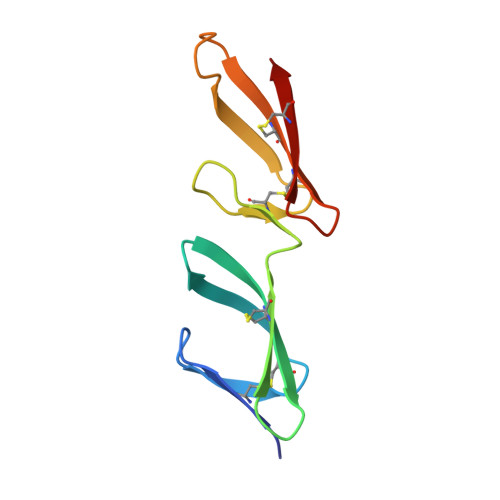
Borrelia burgdorferi Protein BBK32 Binds to Soluble Fibronectin via the N-terminal 70-kDa Region, Causing Fibronectin to Undergo Conformational Extension.
Harris, G., Ma, W., Maurer, L.M., Potts, J.R., Mosher, D.F.(2014) J Biological Chem 289: 22490-22499
- PubMed: 24962582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.578419
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PZ5 - PubMed Abstract:
BBK32 is a fibronectin (FN)-binding protein expressed on the cell surface of Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease. There is conflicting information about where and how BBK32 interacts with FN. We have characterized interactions of a recombinant 86-mer polypeptide, "Bbk32," comprising the unstructured FN-binding region of BBK32. Competitive enzyme-linked assays utilizing various FN fragments and epitope-mapped anti-FN monoclonal antibodies showed that Bbk32 binding involves both the fibrin-binding and the gelatin-binding domains of the 70-kDa N-terminal region (FN70K). Crystallographic and NMR analyses of smaller Bbk32 peptides complexed, respectively, with (2-3)FNI and (8-9)FNI, demonstrated that binding occurs by β-strand addition. Isothermal titration calorimetry indicated that Bbk32 binds to isolated FN70K more tightly than to intact FN. In a competitive enzyme-linked binding assay, complex formation with Bbk32 enhanced binding of FN with mAbIII-10 to the (10)FNIII module. Thus, Bbk32 binds to multiple FN type 1 modules of the FN70K region by a tandem β-zipper mechanism, and in doing so increases accessibility of FNIII modules that interact with other ligands. The similarity in the FN-binding mechanism of BBK32 and previously studied streptococcal proteins suggests that the binding and associated conformational change of FN play a role in infection.
- From the Department of Biology, University of York, York YO10 5DD, United Kingdom and.
Organizational Affiliation: