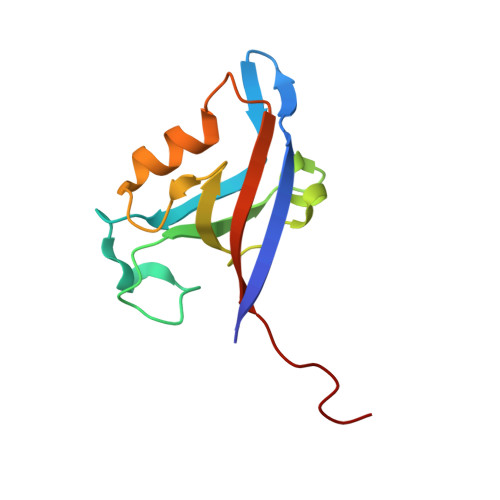
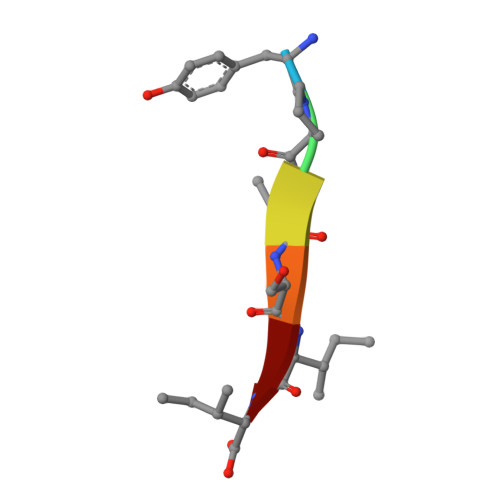
Sequence Engineering at Non-motif Modulator Residues Yields a Peptide That Effectively Targets a Single PDZ Protein in a Disease-relevant Cellular Context.
Amacher, J.F., Cushing, P.R., Vouilleme, L., Cullati, S.N., Deng, B., Gerber, S.A., Boisguerin, P., Madden, D.R.(2026) J Mol Biology 438: 169597-169597
- PubMed: 41419168
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169597
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SFJ, 4NNL, 4NNM, 4Q6S - PubMed Abstract:
PDZ interaction networks are finely-tuned products of evolution. These widespread binding domains recognize short linear motifs (SLiMs), usually at the C-terminus of their interacting partners, and are involved in trafficking and signaling pathways, the formation of tight junctions, and scaffolding of the post-synaptic density of neurons, amongst other roles. Typically, a single PDZ domain binds multiple targets; conversely, each PDZ-binding protein engages several PDZ domains, dependent on cellular conditions. Historical PDZ binding motifs rely on two key positions for binding. However, previous insights on modulator, or non-motif, selectivity preferences reveal that these limited motifs are insufficient to describe PDZ-mediated interactomes, consistent with the observation that the degree of promiscuity is much more limited than predicted by defined binding classes. Here, we use these principles to engineer and test a peptide-based inhibitor capable of interacting with a single PDZ domain-containing protein in a disease-relevant cellular system. We first interrogate a previously developed sequence selective for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)-Associated Ligand (CAL), one of five PDZ domains known to bind the CFTR C-terminus, probing for off-target PDZ partners. Once identified, we use parallel biochemical and structural refinement to eliminate these interactions and introduce a CAL PDZ inhibitor with unprecedented PDZ domain selectivity. We test and verify specificity using relevant cellular PDZ target networks in a mass spectrometry-based approach. Our resultant selective inhibitor enhances chloride efflux when applied to polarized patient bronchial epithelial cells, as well as confirms that engineering an effectively single-PDZ peptide is possible when modulator preferences are applied.
- Dept. of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, NH 03755, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: