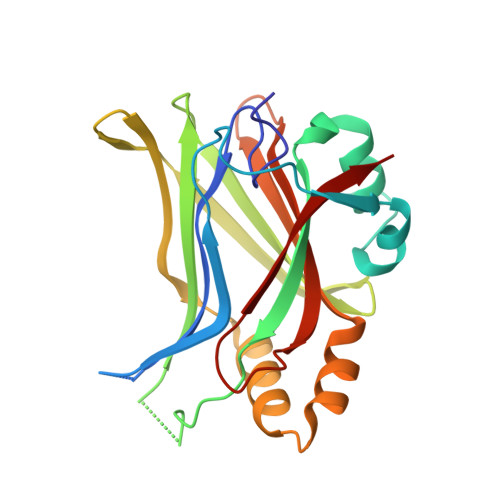
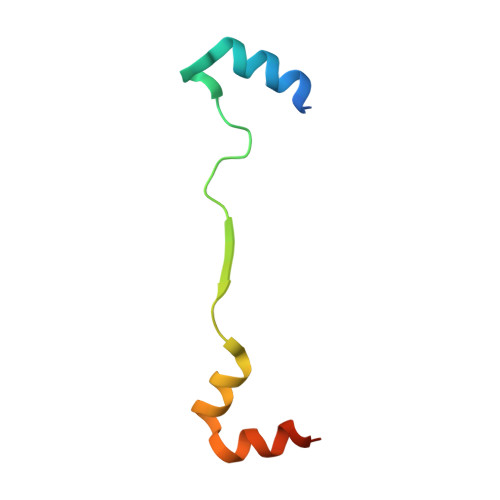
A Peptide Mimicking VGLL4 Function Acts as a YAP Antagonist Therapy against Gastric Cancer.
Jiao, S., Wang, H., Shi, Z., Dong, A., Zhang, W., Song, X., He, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Wang, X., Guo, T., Li, P., Zhao, Y., Ji, H., Zhang, L., Zhou, Z.(2014) Cancer Cell 25: 166-180
- PubMed: 24525233
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LN0 - PubMed Abstract:
The Hippo pathway has been implicated in suppressing tissue overgrowth and tumor formation by restricting the oncogenic activity of YAP. However, transcriptional regulators that inhibit YAP activity have not been well studied. Here, we uncover clinical importance for VGLL4 in gastric cancer suppression and find that VGLL4 directly competes with YAP for binding TEADs. Importantly, VGLL4's tandem Tondu domains are not only essential but also sufficient for its inhibitory activity toward YAP. A peptide mimicking this function of VGLL4 potently suppressed tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. These findings suggest that disruption of YAP-TEADs interaction by a VGLL4-mimicking peptide may be a promising therapeutic strategy against YAP-driven human cancers.
- National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 320 Yue-Yang Road, Shanghai 200031, China.
Organizational Affiliation: