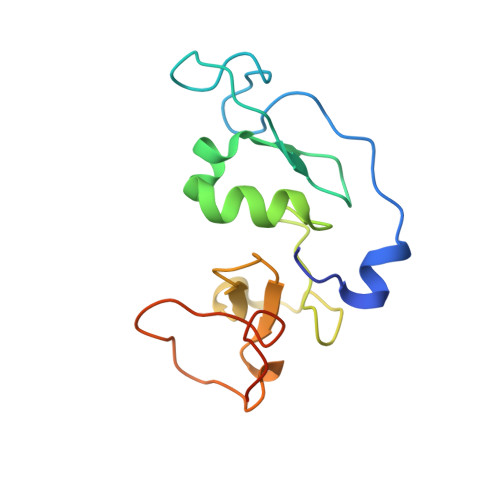
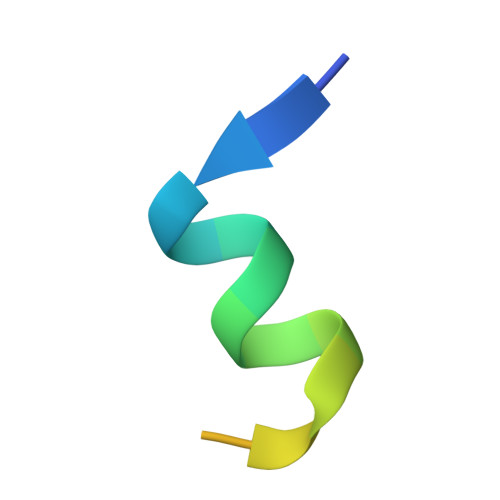
The double PHD finger domain of MOZ/MYST3 induces alpha-helical structure of the histone H3 tail to facilitate acetylation and methylation sampling and modification.
Dreveny, I., Deeves, S.E., Fulton, J., Yue, B., Messmer, M., Bhattacharya, A., Collins, H.M., Heery, D.M.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 822-835
- PubMed: 24150941
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt931
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LJN, 4LK9, 4LKA, 4LLB - PubMed Abstract:
Histone tail modifications control many nuclear processes by dictating the dynamic exchange of regulatory proteins on chromatin. Here we report novel insights into histone H3 tail structure in complex with the double PHD finger (DPF) of the lysine acetyltransferase MOZ/MYST3/KAT6A. In addition to sampling H3 and H4 modification status, we show that the DPF cooperates with the MYST domain to promote H3K9 and H3K14 acetylation, although not if H3K4 is trimethylated. Four crystal structures of an extended DPF alone and in complex with unmodified or acetylated forms of the H3 tail reveal the molecular basis of crosstalk between H3K4me3 and H3K14ac. We show for the first time that MOZ DPF induces α-helical conformation of H3K4-T11, revealing a unique mode of H3 recognition. The helical structure facilitates sampling of H3K4 methylation status, and proffers H3K9 and other residues for modification. Additionally, we show that a conserved double glycine hinge flanking the H3 tail helix is required for a conformational change enabling docking of H3K14ac with the DPF. In summary, our data provide the first observations of extensive helical structure in a histone tail, revealing the inherent ability of the H3 tail to adopt alternate conformations in complex with chromatin regulators.
- Centre for Biomolecular Sciences, School of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham, Nottingham NG7 2RD, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: