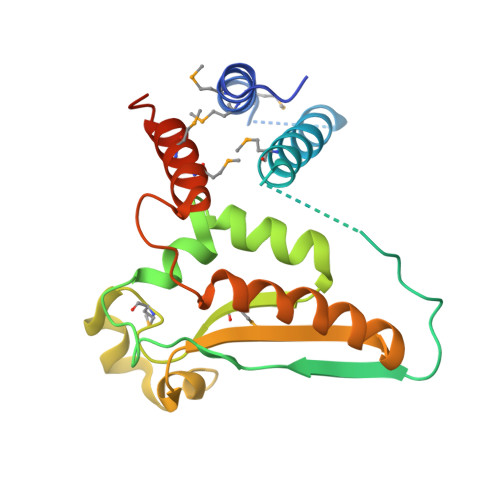
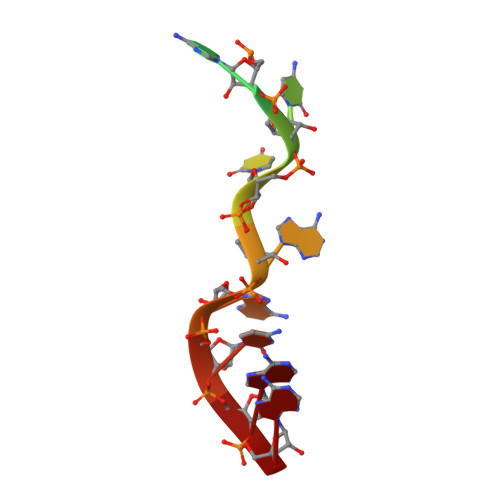
Structure-function studies of STAR family Quaking proteins bound to their in vivo RNA target sites.
Teplova, M., Hafner, M., Teplov, D., Essig, K., Tuschl, T., Patel, D.J.(2013) Genes Dev 27: 928-940
- PubMed: 23630077
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.216531.113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JVH, 4JVY - PubMed Abstract:
Mammalian Quaking (QKI) and its Caenorhabditis elegans homolog, GLD-1 (defective in germ line development), are evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins, which post-transcriptionally regulate target genes essential for developmental processes and myelination. We present X-ray structures of the STAR (signal transduction and activation of RNA) domain, composed of Qua1, K homology (KH), and Qua2 motifs of QKI and GLD-1 bound to high-affinity in vivo RNA targets containing YUAAY RNA recognition elements (RREs). The KH and Qua2 motifs of the STAR domain synergize to specifically interact with bases and sugar-phosphate backbones of the bound RRE. Qua1-mediated homodimerization generates a scaffold that enables concurrent recognition of two RREs, thereby plausibly targeting tandem RREs present in many QKI-targeted transcripts. Structure-guided mutations reduced QKI RNA-binding affinity in vitro and in vivo, and expression of QKI mutants in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) significantly decreased the abundance of QKI target mRNAs. Overall, our studies define principles underlying RNA target selection by STAR homodimers and provide insights into the post-transcriptional regulatory function of mammalian QKI proteins.
- Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York 10065, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: