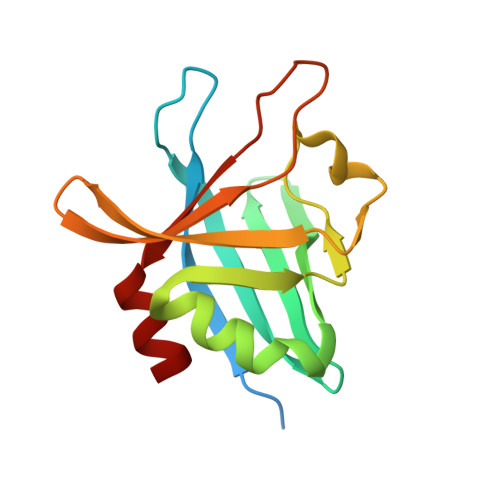
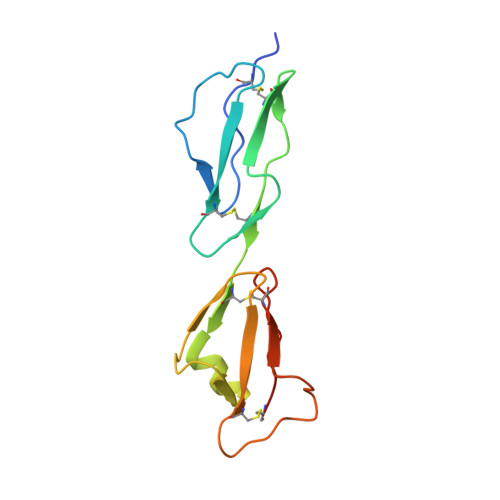
Structural Basis for Complement Evasion by Lyme Disease Pathogen Borrelia burgdorferi
Bhattacharjee, A., Oeemig, J.S., Kolodziejczyk, R., Meri, T., Kajander, T., Lehtinen, M.J., Iwai, H., Jokiranta, T.S., Goldman, A.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 18685-18695
- PubMed: 23658013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.459040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2M4F, 4J38 - PubMed Abstract:
Borrelia burgdorferi spirochetes that cause Lyme borreliosis survive for a long time in human serum because they successfully evade the complement system, an important arm of innate immunity. The outer surface protein E (OspE) of B. burgdorferi is needed for this because it recruits complement regulator factor H (FH) onto the bacterial surface to evade complement-mediated cell lysis. To understand this process at the molecular level, we used a structural approach. First, we solved the solution structure of OspE by NMR, revealing a fold that has not been seen before in proteins involved in complement regulation. Next, we solved the x-ray structure of the complex between OspE and the FH C-terminal domains 19 and 20 (FH19-20) at 2.83 Å resolution. The structure shows that OspE binds FH19-20 in a way similar to, but not identical with, that used by endothelial cells to bind FH via glycosaminoglycans. The observed interaction of OspE with FH19-20 allows the full function of FH in down-regulation of complement activation on the bacteria. This reveals the molecular basis for how B. burgdorferi evades innate immunity and suggests how OspE could be used as a potential vaccine antigen.
- Haartman Institute, Department of Bacteriology and Immunology, and Research Programs Unit, Immunobiology, University of Helsinki, FIN-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
Organizational Affiliation: