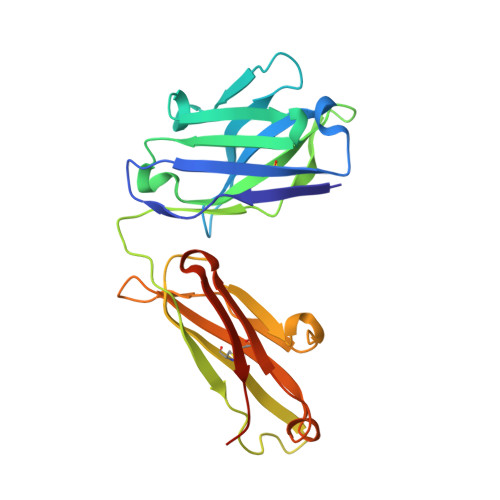
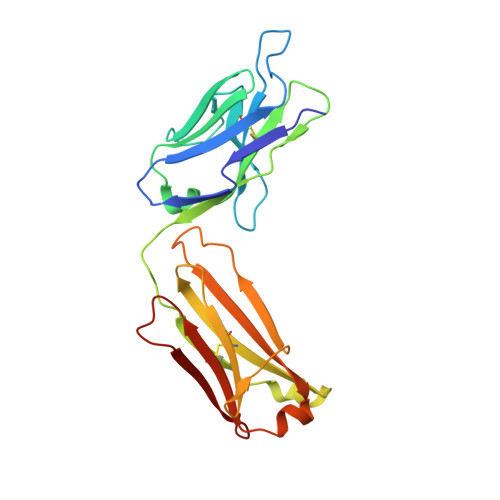
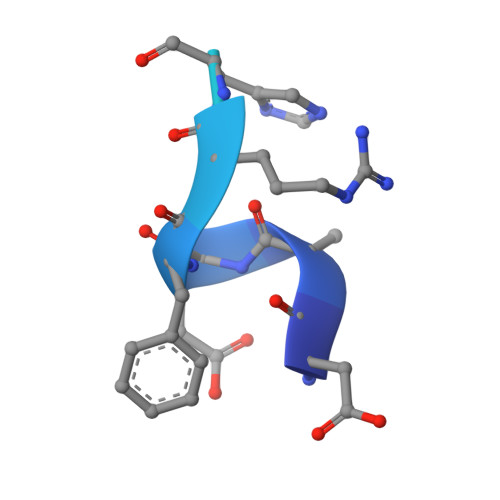
Bapineuzumab captures the N-terminus of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta peptide in a helical conformation.
Miles, L.A., Crespi, G.A., Doughty, L., Parker, M.W.(2013) Sci Rep 3: 1302-1302
- PubMed: 23416764
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01302
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HIX - PubMed Abstract:
Bapineuzumab is a humanized antibody developed by Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson targeting the amyloid (Aβ) plaques that underlie Alzheimer's disease neuropathology. Here we report the crystal structure of a Fab-Aβ peptide complex that reveals Bapineuzumab surprisingly captures Aβ in a monomeric helical conformation at the N-terminus. Microscale thermophoresis suggests that the Fab binds soluble Aβ(1-40) with a K(D) of 89 (±9) nM. The structure explains the antibody's exquisite selectivity for particular Aβ species and why it cannot recognize N-terminally modified or truncated Aβ peptides.
- ACRF Rational Drug Discovery Centre and Biota Structural Biology Laboratory, St. Vincent's Institute of Medical Research, Fitzroy, Victoria 3056, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: