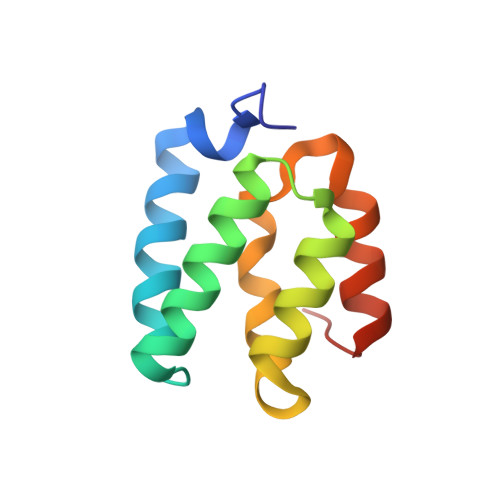
Structural studies of cerebral cavernous malformations 2 (CCM2) reveal a folded helical domain at its C-terminus.
Fisher, O.S., Zhang, R., Li, X., Murphy, J.W., Demeler, B., Boggon, T.J.(2013) FEBS Lett 587: 272-277
- PubMed: 23266514
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.12.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FQN - PubMed Abstract:
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM) are neurovascular dysplasias affecting up to 0.5% of the population. Mutations in the CCM2 gene are associated with acquisition of CCM. We identify a previously uncharacterized domain at the C-terminus of CCM2 and determine its 1.9Å resolution crystal structure. Because this domain is structurally homologous to the N-terminal domain of harmonin, we name it the CCM2 harmonin-homology domain or HHD. CCM2 HHD is observed in two conformations, and we employ analytical ultracentrifugation to test its oligomerization. Additionally, CCM2 HHD contains an unusually long 13-residue 3(10) helix. This study provides the first structural characterization of CCM2.
- Department of Pharmacology, Yale University School of Medicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, CT 06520, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: