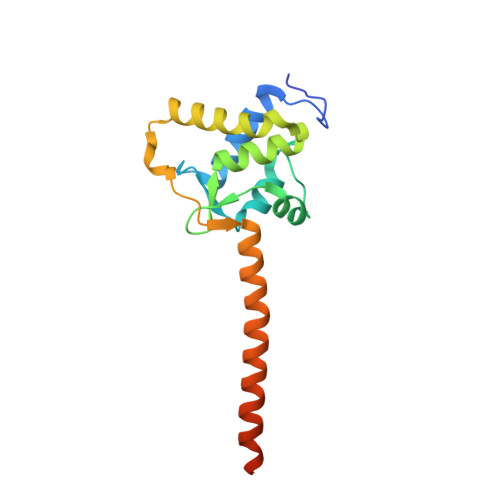
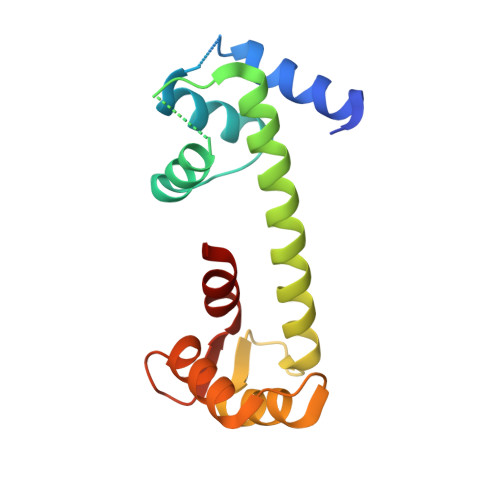
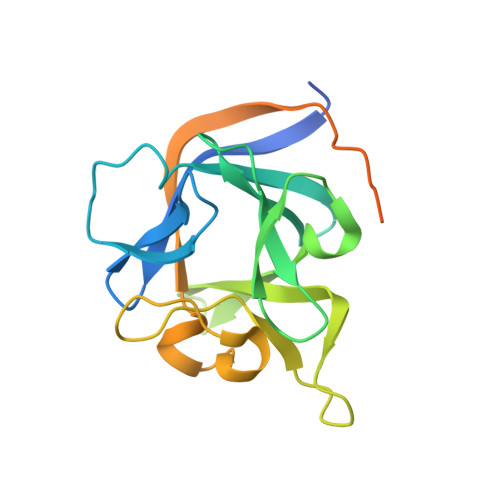
Crystal Structure of the Ternary Complex of a NaV C-Terminal Domain, a Fibroblast Growth Factor Homologous Factor, and Calmodulin.
Wang, C., Chung, B.C., Yan, H., Lee, S.Y., Pitt, G.S.(2012) Structure 20: 1167-1176
- PubMed: 22705208
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.05.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DCK - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated Na⁺ (Na(V)) channels initiate neuronal action potentials. Na(V) channels are composed of a transmembrane domain responsible for voltage-dependent Na⁺ conduction and a cytosolic C-terminal domain (CTD) that regulates channel function through interactions with many auxiliary proteins, including fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs) and calmodulin (CaM). Most ion channel structural studies have focused on mechanisms of permeation and voltage-dependent gating but less is known about how intracellular domains modulate channel function. Here we report the crystal structure of the ternary complex of a human Na(V) CTD, an FHF, and Ca²⁺-free CaM at 2.2 Å. Combined with functional experiments based on structural insights, we present a platform for understanding the roles of these auxiliary proteins in Na(V) channel regulation and the molecular basis of mutations that lead to neuronal and cardiac diseases. Furthermore, we identify a critical interaction that contributes to the specificity of individual Na(V) CTD isoforms for distinctive FHFs.
- Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Duke University Medical Center, 2 Genome Ct, Durham, NC 27710, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: