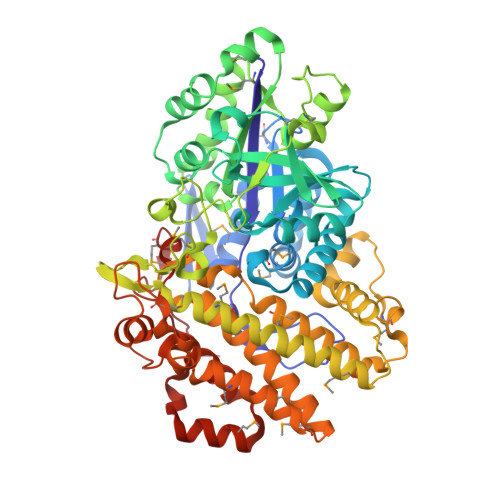
Structural Features Underlying the Selective Cleavage of a Novel Exo-Type Maltose-Forming Amylase from Pyrococcus Sp. St04
Park, K.-H., Jung, J.-H., Park, S.-G., Lee, M.-E., Holden, J.F., Park, C.-S., Woo, E.-J.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 1659
- PubMed: 24914977
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714006567
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CMR - PubMed Abstract:
A novel maltose-forming α-amylase (PSMA) was recently found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus sp. ST04. This enzyme shows <13% amino-acid sequence identity to other known α-amylases and displays a unique enzymatic property in that it hydrolyzes both α-1,4-glucosidic and α-1,6-glucosidic linkages of substrates, recognizing only maltose units, in an exo-type manner. Here, the crystal structure of PSMA at a resolution of 1.8 Å is reported, showing a tight ring-shaped tetramer with monomers composed of two domains: an N-domain (amino acids 1-341) with a typical GH57 family (β/α)7-barrel fold and a C-domain (amino acids 342-597) composed of α-helical bundles. A small closed cavity observed in proximity to the catalytic residues Glu153 and Asp253 at the domain interface has the appropriate volume and geometry to bind a maltose unit, accounting for the selective exo-type maltose hydrolysis of the enzyme. A narrow gate at the putative subsite +1 formed by residue Phe218 and Phe452 is essential for specific cleavage of glucosidic bonds. The closed cavity at the active site is connected to a short substrate-binding channel that extends to the central hole of the tetramer, exhibiting a geometry that is significantly different from classical maltogenic amylases or β-amylases. The structural features of this novel exo-type maltose-forming α-amylase provide a molecular basis for its unique enzymatic characteristics and for its potential use in industrial applications and protein engineering.
- Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Daejeon 305-806, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: