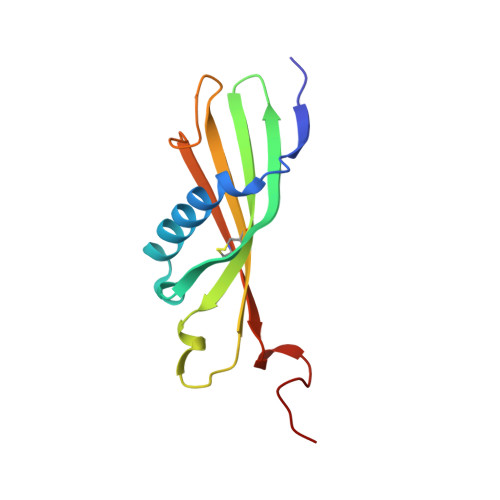
Crystal Structure of Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein N2 Domain Reveals Redox Activity at an Interdomain Disulfide Bridge: Implications for Angiogenic Regulation.
Kassaar, O., Mcmahon, S.A., Thompson, R., Botting, C.H., Naismith, J.H., Stewart, A.J.(2014) Blood 123: 1948
- PubMed: 24501222
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-11-535963
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CCV - PubMed Abstract:
Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) is a plasma protein consisting of 6 distinct functional domains and is an important regulator of key cardiovascular processes, including angiogenesis and coagulation. The protein is composed of 2 N-terminal domains (N1 and N2), 2 proline-rich regions (PRR1 and PRR2) that flank a histidine-rich region (HRR), and a C-terminal domain. To date, structural information of HRG has largely come from sequence analysis and spectroscopic studies. It is thought that an HRG fragment containing the HRR, released via plasmin-mediated cleavage, acts as a negative regulator of angiogenesis in vivo. However, its release also requires cleavage of a disulphide bond suggesting that its activity is mediated by a redox process. Here, we present a 1.93 Å resolution crystal structure of the N2 domain of serum-purified rabbit HRG. The structure confirms that the N2 domain, which along with the N1 domain, forms an important molecular interaction site on HRG, possesses a cystatin-like fold composed of a 5-stranded antiparallel β-sheet wrapped around a 5-turn α-helix. A native N-linked glycosylation site was identified at Asn184. Moreover, the structure reveals the presence of an S-glutathionyl adduct at Cys185, which has implications for the redox-mediated release of the antiangiogenic cleavage product from HRG.
- School of Medicine and.
Organizational Affiliation: