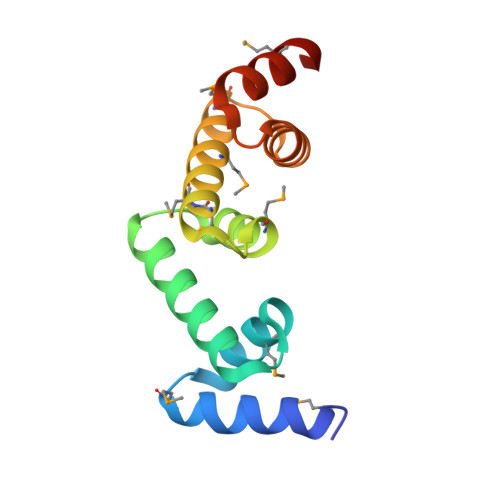
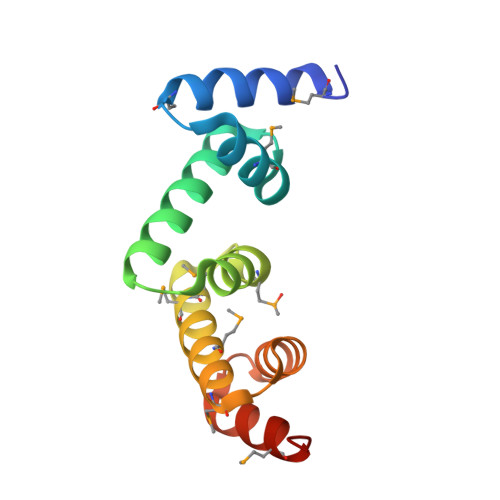
The UBAP1 subunit of ESCRT-I interacts with ubiquitin via a SOUBA domain.
Agromayor, M., Soler, N., Caballe, A., Kueck, T., Freund, S.M., Allen, M.D., Bycroft, M., Perisic, O., Ye, Y., McDonald, B., Scheel, H., Hofmann, K., Neil, S.J., Martin-Serrano, J., Williams, R.L.(2012) Structure 20: 414-428
- PubMed: 22405001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.12.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AE4 - PubMed Abstract:
The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) facilitate endosomal sorting of ubiquitinated cargo, MVB biogenesis, late stages of cytokinesis, and retroviral budding. Here we show that ubiquitin associated protein 1 (UBAP1), a subunit of human ESCRT-I, coassembles in a stable 1:1:1:1 complex with Vps23/TSG101, VPS28, and VPS37. The X-ray crystal structure of the C-terminal region of UBAP1 reveals a domain that we describe as a solenoid of overlapping UBAs (SOUBA). NMR analysis shows that each of the three rigidly arranged overlapping UBAs making up the SOUBA interact with ubiquitin. We demonstrate that UBAP1-containing ESCRT-I is essential for degradation of antiviral cell-surface proteins, such as tetherin (BST-2/CD317), by viral countermeasures, namely, the HIV-1 accessory protein Vpu and the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ubiquitin ligase K5.
- Department of Infectious Diseases, King's College London School of Medicine, London SE1 9RT, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: