Direct contacts between extracellular membrane-proximal domains are required for VEGF receptor activation and cell signaling
Yang, Y., Xie, P., Opatowsky, Y., Schlessinger, J.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 1906-1911
- PubMed: 20080685
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914052107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KVQ - PubMed Abstract:
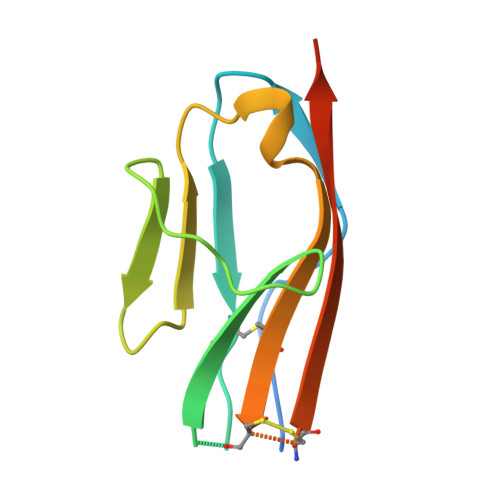
Structural analyses of the extracellular region of stem cell factor (SCF) receptor (also designated KIT) in complex with SCF revealed a sequence motif in a loop in the fourth Ig-like domain (D4) that is responsible for forming homotypic receptor contacts and for ligand-induced KIT activation and cell signaling. An identical motif was identified in the most membrane-proximal seventh Ig-like domain (D7) of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR2, and VEGFR3. In this report we demonstrate that ligand-induced tyrosine autophosphorylation and cell signaling via VEGFR1 or VEGFR2 harboring mutations in critical residues (Arg726 or Asp731) in D7 are strongly impaired. We also describe the crystal structure of D7 of VEGFR2 to a resolution of 2.7 A. The structure shows that homotypic D7 contacts are mediated by salt bridges and van der Waals contacts formed between Arg726 of one protomer and Asp731 of the other protomer. The structure of D7 dimer is very similar to the structure of D4 dimers seen in the crystal structure of KIT extracellular region in complex with SCF. The high similarity between VEGFR D7 and KIT D4 in both structure and function provides further evidence for common ancestral origins of type III and type V RTKs. It also reveals a conserved mechanism for RTK activation and a novel target for pharmacological intervention of pathologically activated RTKs.
- Department of Pharmacology, Yale University School of Medicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, CT 06520, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: