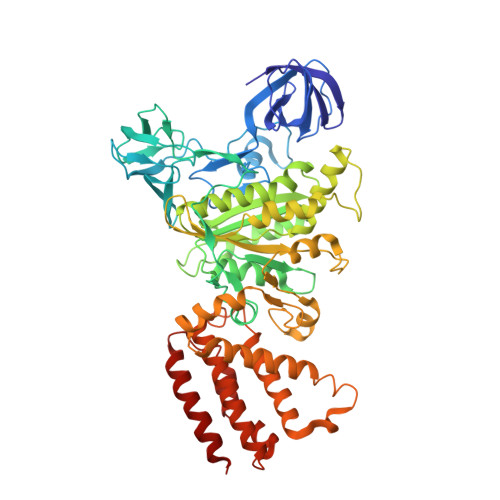
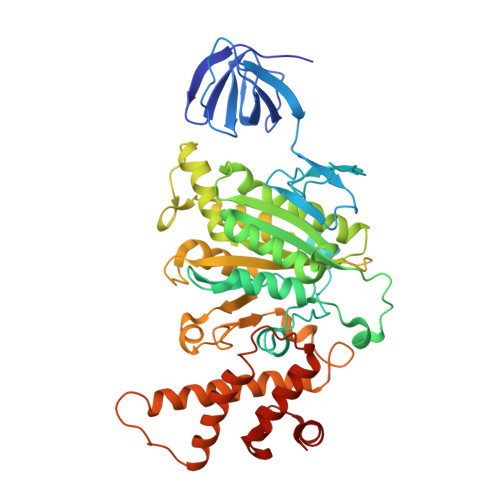
Crystal structure of A(3)B(3) complex of V-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus.
Maher, M.J., Akimoto, S., Iwata, M., Nagata, K., Hori, Y., Yoshida, M., Yokoyama, S., Iwata, S., Yokoyama, K.(2009) EMBO J 28: 3771-3779
- PubMed: 19893485
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GQB - PubMed Abstract:
Vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) exist in various cellular membranes of many organisms to regulate physiological processes by controlling the acidic environment. Here, we have determined the crystal structure of the A(3)B(3) subcomplex of V-ATPase at 2.8 A resolution. The overall construction of the A(3)B(3) subcomplex is significantly different from that of the alpha(3)beta(3) sub-domain in F(o)F(1)-ATP synthase, because of the presence of a protruding 'bulge' domain feature in the catalytic A subunits. The A(3)B(3) subcomplex structure provides the first molecular insight at the catalytic and non-catalytic interfaces, which was not possible in the structures of the separate subunits alone. Specifically, in the non-catalytic interface, the B subunit seems to be incapable of binding ATP, which is a marked difference from the situation indicated by the structure of the F(o)F(1)-ATP synthase. In the catalytic interface, our mutational analysis, on the basis of the A(3)B(3) structure, has highlighted the presence of a cluster composed of key hydrophobic residues, which are essential for ATP hydrolysis by V-ATPases.
- Division of Molecular Biosciences, Imperial College London, South Kensington Campus, London, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: