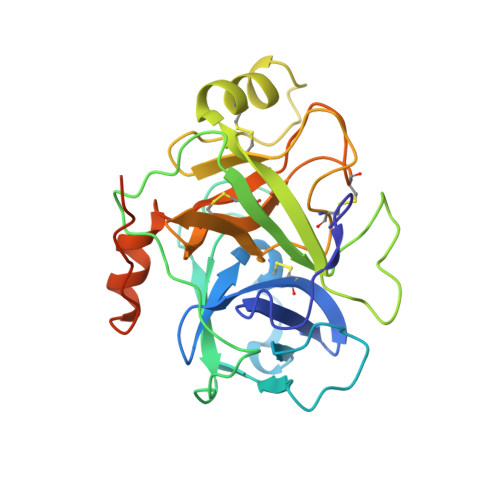
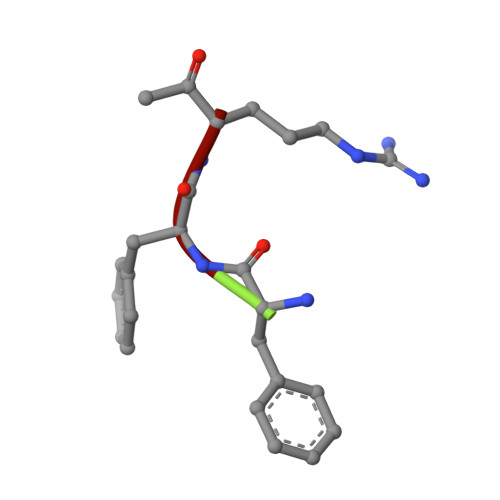
Active site conformational changes of prostasin provide a new mechanism of protease regulation by divalent cations.
Spraggon, G., Hornsby, M., Shipway, A., Tully, D.C., Bursulaya, B., Danahay, H., Harris, J.L., Lesley, S.A.(2009) Protein Sci 18: 1081-1094
- PubMed: 19388054
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3E0N, 3E1X, 3FVF, 3GYL, 3GYM - PubMed Abstract:
Prostasin or human channel-activating protease 1 has been reported to play a critical role in the regulation of extracellular sodium ion transport via its activation of the epithelial cell sodium channel. Here, the structure of the extracellular portion of the membrane associated serine protease has been solved to high resolution in complex with a nonselective d-FFR chloromethyl ketone inhibitor, in an apo form, in a form where the apo crystal has been soaked with the covalent inhibitor camostat and in complex with the protein inhibitor aprotinin. It was also crystallized in the presence of the divalent cation Ca(+2). Comparison of the structures with each other and with other members of the trypsin-like serine protease family reveals unique structural features of prostasin and a large degree of conformational variation within specificity determining loops. Of particular interest is the S1 subsite loop which opens and closes in response to basic residues or divalent ions, directly binding Ca(+2) cations. This induced fit active site provides a new possible mode of regulation of trypsin-like proteases adapted in particular to extracellular regions with variable ionic concentrations such as the outer membrane layer of the epithelial cell.
- Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation, 10675 John Jay Hopkins Drive, San Diego, California 92121, USA. gspraggo@gnf.org
Organizational Affiliation: