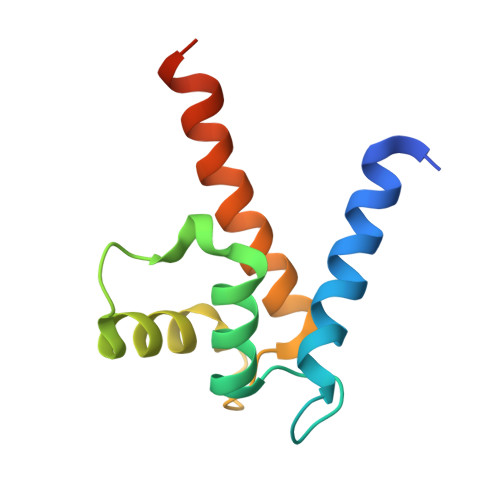
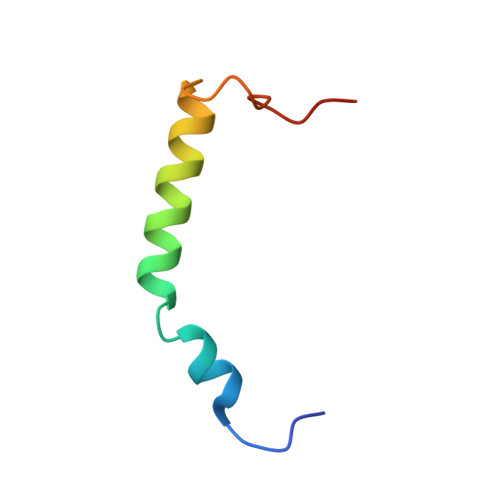
Crystal Structure of the S100A4-Nonmuscle Myosin Iia Tail Fragment Complex Reveals an Asymmetric Target Binding Mechanism.
Kiss, B., Duelli, A., Radnai, L., Kekesi, K.A., Katona, G., Nyitray, L.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 6048
- PubMed: 22460785
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114732109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ZWH - PubMed Abstract:
S100A4 is a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins that is directly involved in tumor metastasis. It binds to the nonmuscle myosin IIA (NMIIA) tail near the assembly competence domain (ACD) promoting filament disassembly, which could be associated with increasing metastatic potential of tumor cells. Here, we investigate the mechanism of S100A4-NMIIA interaction based on binding studies and the crystal structure of S100A4 in complex with a 45-residue-long myosin heavy chain fragment. Interestingly, we also find that S100A4 binds as strongly to a homologous heavy chain fragment of nonmuscle myosin IIC as to NMIIA. The structure of the S100A4-NMIIA complex reveals a unique mode of interaction in the S100 family: A single, predominantly α-helical myosin chain is wrapped around the Ca(2+)-bound S100A4 dimer occupying both hydrophobic binding pockets. Thermal denaturation experiments of coiled-coil forming NMIIA fragments indicate that the coiled-coil partially unwinds upon S100A4 binding. Based on these results, we propose a model for NMIIA filament disassembly: Part of the random coil tailpiece and the C-terminal residues of the coiled-coil are wrapped around an S100A4 dimer disrupting the ACD and resulting in filament dissociation. The description of the complex will facilitate the design of specific drugs that interfere with the S100A4-NMIIA interaction.
- Department of Biochemistry, Eötvös Loránd University, H-1117 Budapest, Hungary.
Organizational Affiliation: