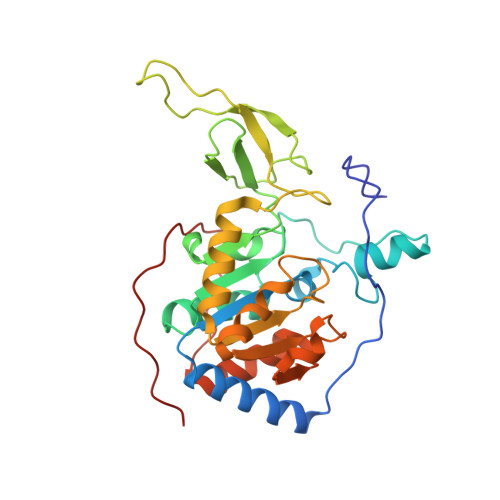
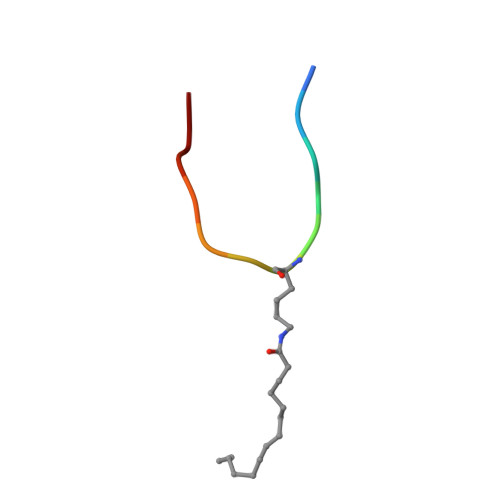
Sirt6 Regulates Tnf-Alpha Secretion Through Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Fatty Acyl Lysine
Jiang, H., Khan, S., Wang, Y., Charron, G., He, B., Sebastian, C., Du, J., Kim, R., Ge, E., Mostoslavsky, R., Hang, H.C., Hao, Q., Lin, H.(2013) Nature 496: 110
- PubMed: 23552949
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ZG6 - PubMed Abstract:
The Sir2 family of enzymes or sirtuins are known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent deacetylases and have been implicated in the regulation of transcription, genome stability, metabolism and lifespan. However, four of the seven mammalian sirtuins have very weak deacetylase activity in vitro. Here we show that human SIRT6 efficiently removes long-chain fatty acyl groups, such as myristoyl, from lysine residues. The crystal structure of SIRT6 reveals a large hydrophobic pocket that can accommodate long-chain fatty acyl groups. We demonstrate further that SIRT6 promotes the secretion of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) by removing the fatty acyl modification on K19 and K20 of TNF-α. Protein lysine fatty acylation has been known to occur in mammalian cells, but the function and regulatory mechanisms of this modification were unknown. Our data indicate that protein lysine fatty acylation is a novel mechanism that regulates protein secretion. The discovery of SIRT6 as an enzyme that controls protein lysine fatty acylation provides new opportunities to investigate the physiological function of a protein post-translational modification that has been little studied until now.
- Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: