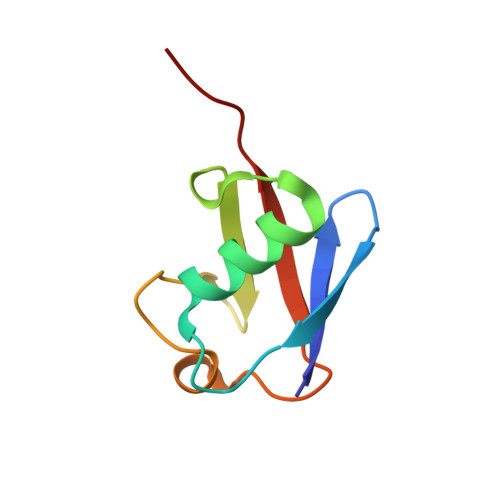
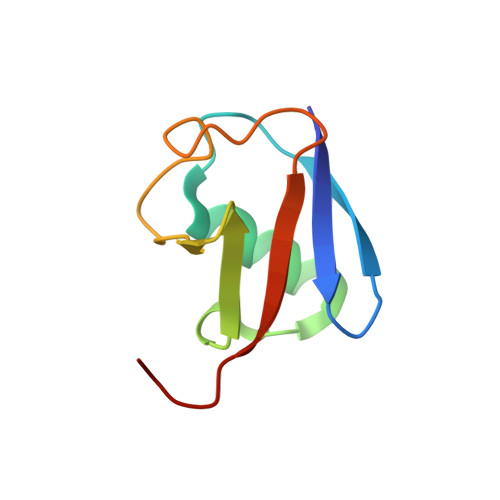
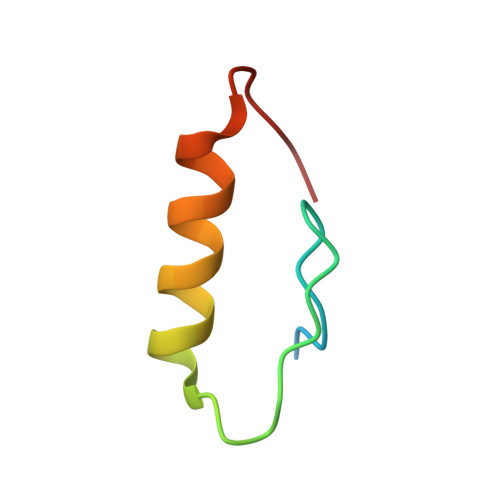
Structural Basis for Ubiquitin Recognition by Ubiquitin-Binding Zinc Finger of FAAP20
Toma, A., Takahashi, T.S., Sato, Y., Yamagata, A., Goto-Ito, S., Nakada, S., Fukuto, A., Horikoshi, Y., Tashiro, S., Fukai, S.(2015) PLoS One 10: e0120887-e0120887
- PubMed: 25799058
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120887
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WWQ - PubMed Abstract:
Several ubiquitin-binding zinc fingers (UBZs) have been reported to preferentially bind K63-linked ubiquitin chains. In particular, the UBZ domain of FAAP20 (FAAP20-UBZ), a member of the Fanconi anemia core complex, seems to recognize K63-linked ubiquitin chains, in order to recruit the complex to DNA interstrand crosslinks and mediate DNA repair. By contrast, it is reported that the attachment of a single ubiquitin to Rev1, a translesion DNA polymerase, increases binding of Rev1 to FAAP20. To clarify the specificity of FAAP20-UBZ, we determined the crystal structure of FAAP20-UBZ in complex with K63-linked diubiquitin at 1.9 Å resolution. In this structure, FAAP20-UBZ interacts only with one of the two ubiquitin moieties. Consistently, binding assays using surface plasmon resonance spectrometry showed that FAAP20-UBZ binds ubiquitin and M1-, K48- and K63-linked diubiquitin chains with similar affinities. Residues in the vicinity of Ala168 within the α-helix and the C-terminal Trp180 interact with the canonical Ile44-centered hydrophobic patch of ubiquitin. Asp164 within the α-helix and the C-terminal loop mediate a hydrogen bond network, which reinforces ubiquitin-binding of FAAP20-UBZ. Mutations of the ubiquitin-interacting residues disrupted binding to ubiquitin in vitro and abolished the accumulation of FAAP20 to DNA damage sites in vivo. Finally, structural comparison among FAAP20-UBZ, WRNIP1-UBZ and RAD18-UBZ revealed distinct modes of ubiquitin binding. UBZ family proteins could be divided into at least three classes, according to their ubiquitin-binding modes.
- Structural Biology Laboratory, Life Science Division, Synchrotron Radiation Research Organization and Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, 113-0032, Japan; Department of Medical Genome Sciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Chiba, 277-8501, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: