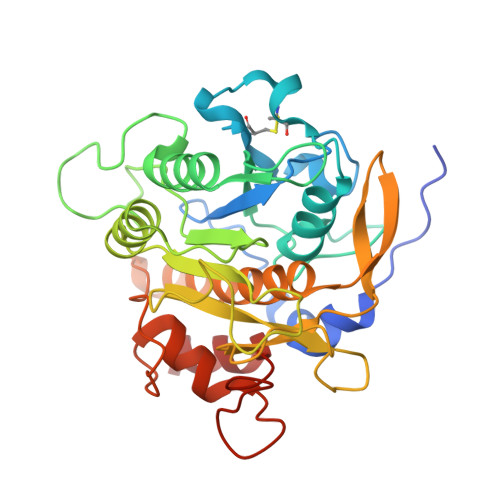
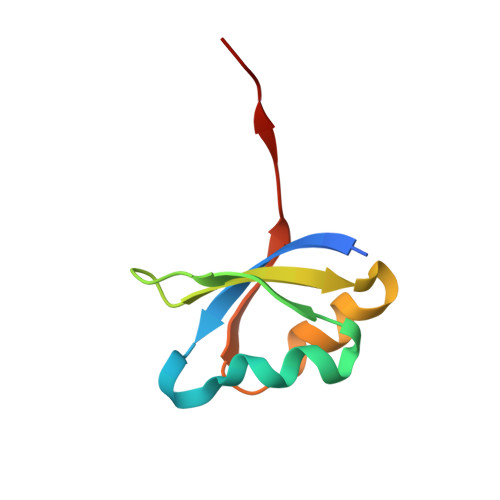
Accelerated maturation of Tk-subtilisin by a Leu Pro mutation at the C-terminus of the propeptide, which reduces the binding of the propeptide to Tk-subtilisin
Uehara, R., Ueda, Y., You, D.J., Koga, Y., Kanaya, S.(2013) FEBS J 280: 994-1006
- PubMed: 23237738
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12091
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VV2 - PubMed Abstract:
Tk-subtilisin, a subtilisin homologue (Gly70-Gly398) from Thermococcus kodakarensis, is matured from its precursor, Pro-Tk-subtilisin [Tk-subtilisin in a pro form (Gly1-Gly398)], by autoprocessing and degradation of propeptide [Tk-propeptide, a propeptide of Tk-subtilisin (Gly1-Leu69)]. The scissile peptide bond between Leu69 and Gly70 of Pro-Tk-subtilisin is first self-cleaved to produce an inactive Tk-propeptide:Tk-subtilisin complex, in which the C-terminal region of Tk-propeptide binds to the active-site cleft of Tk-subtilisin. Tk-propeptide is then dissociated from Tk-subtilisin and degraded by Tk-subtilisin to release active Tk-subtilisin. To examine whether the mutation of Leu69 to Pro, which is the most unfavourable residue in the P1 position for subtilisins, affects the maturation of Pro-Tk-subtilisin, the Pro-Tk-subtilisin and Tk-propeptide derivatives with this mutation (Pro-L69P and L69P-propeptide) were constructed and characterized. Pro-L69P was autoprocessed more slowly than Pro-Tk-subtilisin. Nevertheless, it matured to Tk-subtilisin more rapidly than Pro-Tk-subtilisin because L69P-propeptide was degraded by Tk-subtilisin more rapidly than Tk-propeptide. The chaperone function and stability of L69P-propeptide were comparable to those of Tk-propeptide, whereas the inhibitory potency and binding ability of L69P-propeptide were considerably reduced compared to those of Tk-propeptide. The crystal structure of the complex between L69P-propeptide and S324A-subtilisin (i.e. a protease activity-defective mutant) revealed that the C-terminal region of L69P-propeptide does not well fit into the substrate binding pockets of Tk-subtilisin (S1-S4 subsites) as a result of a conformational change caused by the mutation. These results suggest that the Leu→Pro mutation accelerates the maturation of Pro-Tk-subtilisin by reducing the binding ability of Tk-propeptide to Tk-subtilisin.
- Department of Material and Life Science, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: