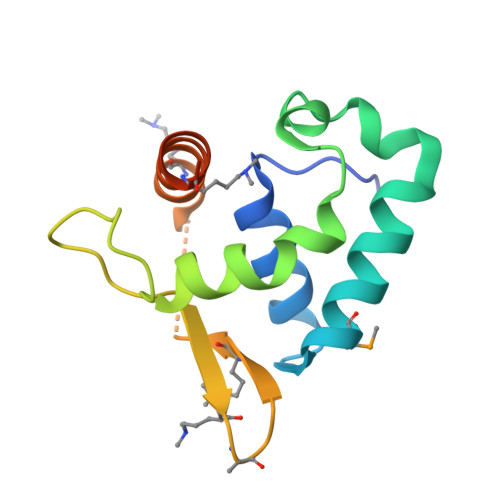
Structure of a Novel Winged-Helix Like Domain from Human NFRKB Protein.
Kumar, A., Mocklinghoff, S., Yumoto, F., Jaroszewski, L., Farr, C.L., Grzechnik, A., Nguyen, P., Weichenberger, C.X., Chiu, H.J., Klock, H.E., Elsliger, M.A., Deacon, A.M., Godzik, A., Lesley, S.A., Conklin, B.R., Fletterick, R.J., Wilson, I.A.(2012) PLoS One 7: e43761-e43761
- PubMed: 22984442
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043761
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3U21 - PubMed Abstract:
The human nuclear factor related to kappa-B-binding protein (NFRKB) is a 1299-residue protein that is a component of the metazoan INO80 complex involved in chromatin remodeling, transcription regulation, DNA replication and DNA repair. Although full length NFRKB is predicted to be around 65% disordered, comparative sequence analysis identified several potentially structured sections in the N-terminal region of the protein. These regions were targeted for crystallographic studies, and the structure of one of these regions spanning residues 370-495 was determined using the JCSG high-throughput structure determination pipeline. The structure reveals a novel, mostly helical domain reminiscent of the winged-helix fold typically involved in DNA binding. However, further analysis shows that this domain does not bind DNA, suggesting it may belong to a small group of winged-helix domains involved in protein-protein interactions.
- Joint Center for Structural Genomics, La Jolla, California, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: