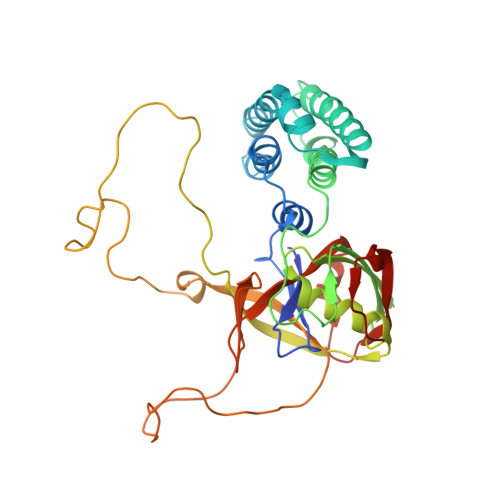
Crystal structure of Arabidopsis cyclophilin38 reveals a previously uncharacterized immunophilin fold and a possible autoinhibitory mechanism.
Vasudevan, D., Fu, A., Luan, S., Swaminathan, K.(2012) Plant Cell 24: 2666-2674
- PubMed: 22706283
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.093781
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RFY - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclophilin38 (CYP38) is one of the highly divergent cyclophilins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Here, we report the crystal structure of the At-CYP38 protein (residues 83 to 437 of 437 amino acids) at 2.39-Å resolution. The structure reveals two distinct domains: an N-terminal helical bundle and a C-terminal cyclophilin β-barrel, connected by an acidic loop. Two N-terminal β-strands become part of the C-terminal cyclophilin β-barrel, thereby making a previously undiscovered domain organization. This study shows that CYP38 does not possess peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase activity and identifies a possible interaction of CYP38 with the E-loop of chlorophyll protein47 (CP47), a component of photosystem II. The interaction of CYP38 with the E-loop of CP47 is mediated through its cyclophilin domain. The N-terminal helical domain is closely packed together with the putative C-terminal cyclophilin domain and establishes a strong intramolecular interaction, thereby preventing the access of the cyclophilin domain to other proteins. This was further verified by protein-protein interaction assays using the yeast two-hybrid system. Furthermore, the non-Leucine zipper N-terminal helical bundle contains several new elements for protein-protein interaction that may be of functional significance. Together, this study provides the structure of a plant cyclophilin and explains a possible mechanism for autoinhibition of its function through an intramolecular interaction.
- Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543.
Organizational Affiliation: