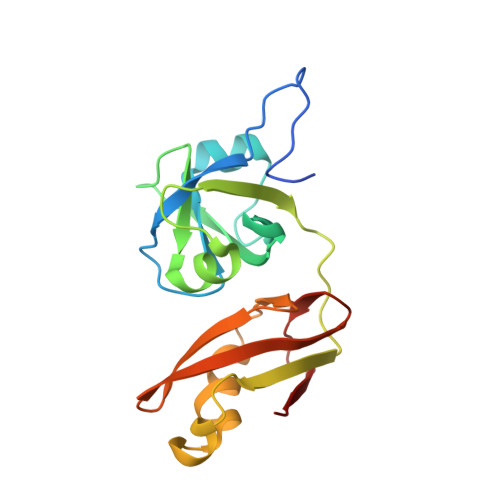
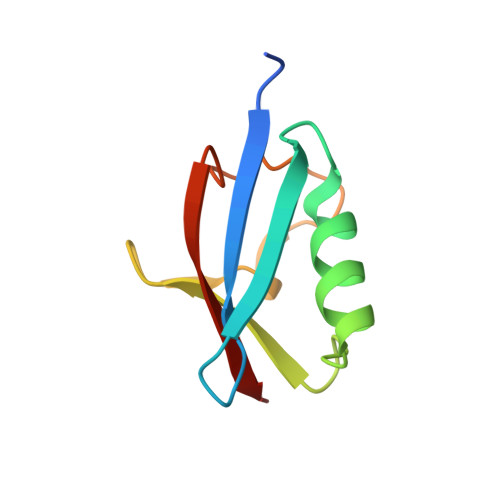
Hierarchical Binding of Cofactors to the AAA ATPase p97.
Hanzelmann, P., Buchberger, A., Schindelin, H.(2011) Structure 19: 833-843
- PubMed: 21645854
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.03.018
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QQ7, 3QQ8, 3R3M - PubMed Abstract:
The hexameric AAA ATPase p97 is involved in several human proteinopathies and mediates ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation among other essential cellular processes. Via its N-terminal domain (N domain), p97 interacts with multiple regulatory cofactors including the UFD1/NPL4 heterodimer and members of the "ubiquitin regulatory X" (UBX) domain protein family; however, the principles governing cofactor selectivity remain to be deciphered. Our crystal structure of the FAS-associated factor 1 (FAF1)UBX domain in complex with the p97N domain reveals that the signature Phe-Pro-Arg motif known to be crucial for interactions of UBX domains with p97 adopts a cis-proline configuration, in contrast to a cis-trans mixture we derive for the isolated FAF1UBX domain. Biochemical studies confirm that binding critically depends on a proline at this position. Furthermore, we observe that the UBX proteins FAF1 and UBXD7 only bind to p97-UFD1/NPL4, but not free p97, thus demonstrating for the first time a hierarchy in p97-cofactor interactions.
- Rudolf Virchow Center for Experimental Biomedicine, University of Würzburg, Josef-Schneider-Str. 2, 97080 Würzburg, Germany. petra.haenzelmann@virchow.uni-wuerzburg.de
Organizational Affiliation: