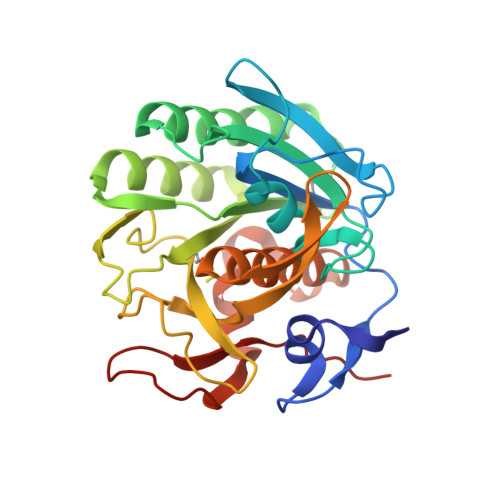
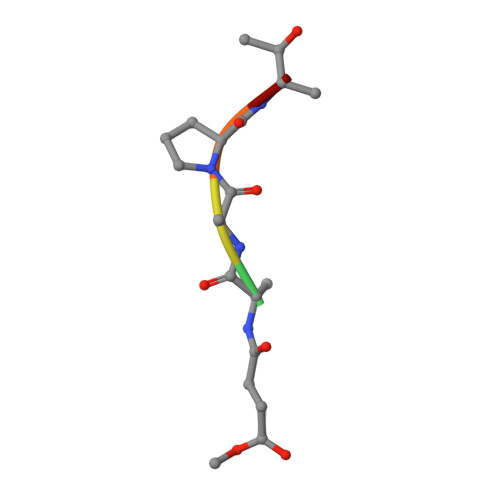
Inhibition of proteinase K by methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Ala-chloromethyl ketone. An x-ray study at 2.2-A resolution.
Wolf, W.M., Bajorath, J., Muller, A., Raghunathan, S., Singh, T.P., Hinrichs, W., Saenger, W.(1991) J Biological Chem 266: 17695-17699
- PubMed: 1894649
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb3prk/pdb
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3PRK - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the transition state analog complex formed covalently between proteinase K and methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Ala-chloromethyl ketone was determined by x-ray diffraction methods at a resolution of 2.2 A and refined by constrained least squares to an R factor of 19.8% for the 11864 structure amplitudes greater than 1 sigma F. The chloromethyl ketone group is covalently linked with the active site functional groups His69(N epsilon) and Ser224(O gamma). The former has substituted for chlorine and the latter has attacked the carbon of the ketone group, thereby forming the tetrahedral carbon atom of the transition state analog. The peptide part of the inhibitor is in an extended conformation and fills subsites S1 to S5 of the substrate recognition site. Its backbone hydrogens bond with strands 100-104 and 132-136 of the substrate recognition site as the central strand of a three-stranded antiparallel beta-pleated sheet. This sheet formation is associated with a movement by approximately 1 A of strand 100-104 which is probably associated with the insertion of the bulky proline side chain. The methoxysuccinyl group is stacked on the phenolic side chain of Tyr104 that is a part of the bottom of the recognition site. Biochemical studies show that shorter inhibitors of this type are less effective than the longer one, because there are fewer hydrogen bonding and van der Waals/stacking interactions.
- Institut für Kristallographie, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: