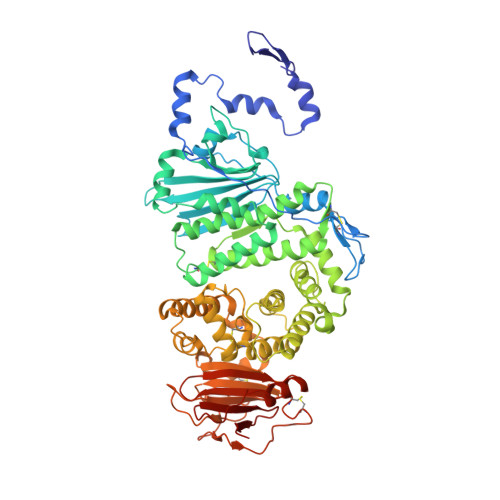
Crystal structure of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) glycoprotein H/glycoprotein L (gH/gL) complex.
Matsuura, H., Kirschner, A.N., Longnecker, R., Jardetzky, T.S.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 22641-22646
- PubMed: 21149717
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1011806108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3PHF - PubMed Abstract:
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a γ-herpesvirus that infects B cells and epithelial cells and that has been linked to malignancies in both cell types in vivo. EBV, like other herpesviruses, has three glycoproteins, glycoprotein B (gB), gH, and gL, that form the core membrane fusion machinery mediating viral penetration into the cell. The gH and gL proteins associate to form a heterodimeric complex, which is necessary for efficient membrane fusion and also implicated in direct binding to epithelial cell receptors required for viral entry. To gain insight into the mechanistic role of gH/gL, we determined the crystal structure of the EBV gH/gL complex. The structure is comprised of four domains organized along the longest axis of the molecule. Comparisons with homologous HSV-2 gH/gL and partial pseudorabies virus gH structures support the domain boundaries determined for the EBV gH/gL structure and illustrate significant differences in interdomain packing angles. The gL subunit and N-terminal residues of gH form a globular domain at one end of the structure, implicated in interactions with gB and activation of membrane fusion. The C-terminal domain of gH, proximal to the viral membrane, is also implicated in membrane fusion. The gH/gL structure locates an integrin binding motif, implicated in epithelial cell entry, on a prominent loop in the central region of the structure. Multiple regions of gH/gL, including its two extreme ends, are functionally important, consistent with the multiple roles of gH/gL in EBV entry.
- Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: