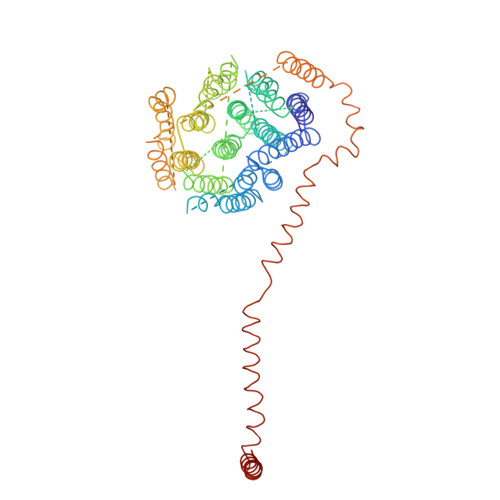
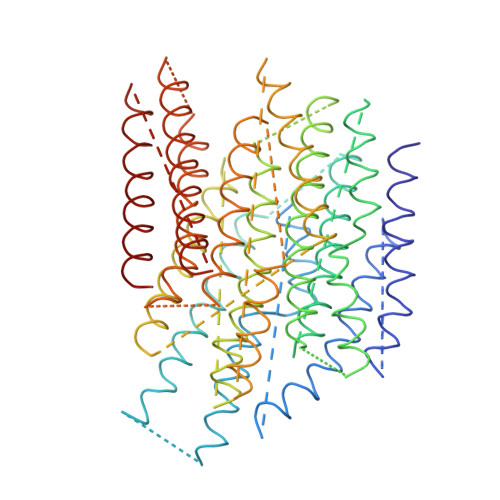
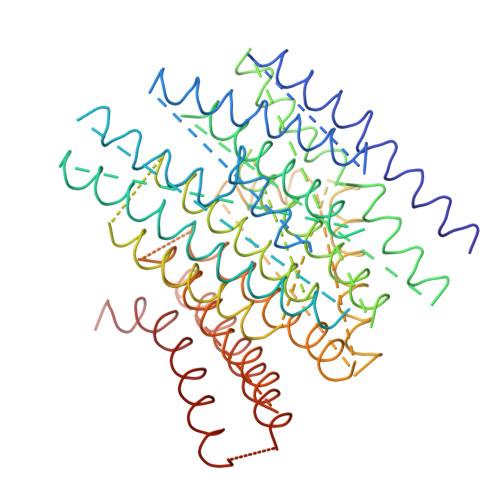
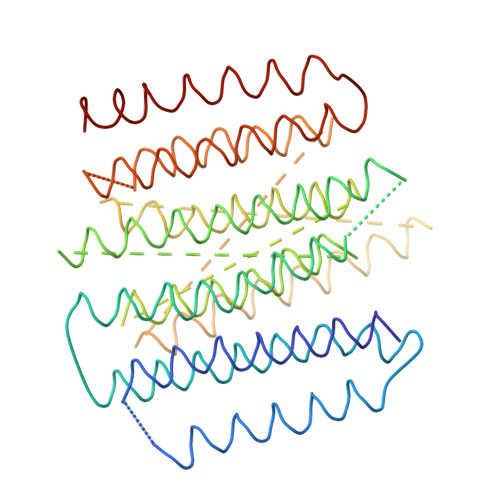
The architecture of respiratory complex I
Efremov, R.G., Baradaran, R., Sazanov, L.A.(2010) Nature 465: 441-445
- PubMed: 20505720
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09066
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3M9C, 3M9S - PubMed Abstract:
Complex I is the first enzyme of the respiratory chain and has a central role in cellular energy production, coupling electron transfer between NADH and quinone to proton translocation by an unknown mechanism. Dysfunction of complex I has been implicated in many human neurodegenerative diseases. We have determined the structure of its hydrophilic domain previously. Here, we report the alpha-helical structure of the membrane domain of complex I from Escherichia coli at 3.9 A resolution. The antiporter-like subunits NuoL/M/N each contain 14 conserved transmembrane (TM) helices. Two of them are discontinuous, as in some transporters. Unexpectedly, subunit NuoL also contains a 110-A long amphipathic alpha-helix, spanning almost the entire length of the domain. Furthermore, we have determined the structure of the entire complex I from Thermus thermophilus at 4.5 A resolution. The L-shaped assembly consists of the alpha-helical model for the membrane domain, with 63 TM helices, and the known structure of the hydrophilic domain. The architecture of the complex provides strong clues about the coupling mechanism: the conformational changes at the interface of the two main domains may drive the long amphipathic alpha-helix of NuoL in a piston-like motion, tilting nearby discontinuous TM helices, resulting in proton translocation.
- Medical Research Council Mitochondrial Biology Unit, Wellcome Trust/MRC Building, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 0XY, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: