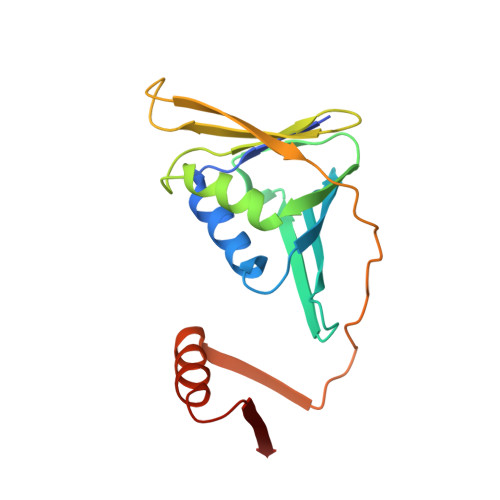
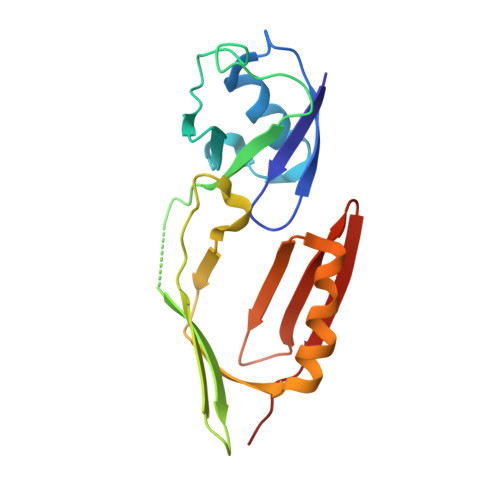Structure of monoubiquitinated PCNA and implications for translesion synthesis and DNA polymerase exchange.
Freudenthal, B.D., Gakhar, L., Ramaswamy, S., Washington, M.T.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 479-484
- PubMed: 20305653
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1776
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3L0W, 3L0X, 3L10 - PubMed Abstract:
DNA synthesis by classical polymerases can be blocked by many lesions. These blocks are overcome by translesion synthesis, whereby the stalled classical, replicative polymerase is replaced by a nonclassical polymerase. In eukaryotes this polymerase exchange requires proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) monoubiquitination. To better understand the polymerase exchange, we developed a means of producing monoubiquitinated PCNA, by splitting the protein into two self-assembling polypeptides. We determined the X-ray crystal structure of monoubiquitinated PCNA and found that the ubiquitin moieties are located on the back face of PCNA and interact with it through their canonical hydrophobic surface. Moreover, the attachment of ubiquitin does not change PCNA's conformation. We propose that PCNA ubiquitination facilitates nonclassical polymerase recruitment to the back of PCNA by forming a new binding surface for nonclassical polymerases, consistent with a 'tool belt' model of the polymerase exchange.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Iowa College of Medicine, Iowa City, Iowa, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: