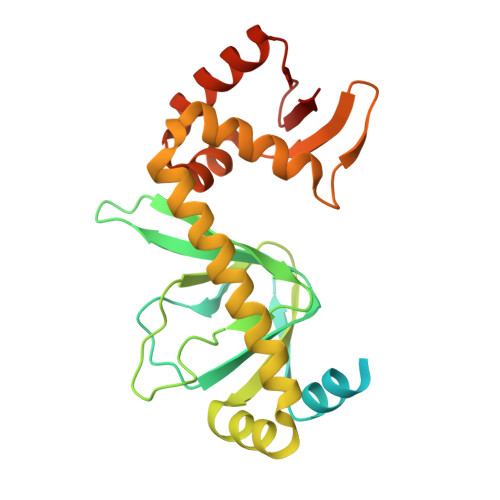
The 1.6A resolution structure of activated D138L mutant of catabolite gene activator protein with two cAMP bound in each monomer
Tao, W.B., Gao, Z.Q., Gao, Z.Y., Zhou, J.H., Huang, Z.X., Dong, Y.H., Yu, S.N.(2011) Int J Biol Macromol 48: 459-465
- PubMed: 21255606
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.01.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KCC - PubMed Abstract:
The X-ray crystal structure of the cAMP-liganded D138L mutant of Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) was determined at a resolution of 1.66Å. This high resolution crystal structure reveals four cAMP binding sites in the homodimer. Two anti conformations of cAMPs (anti-cAMP) locate between the β-barrel and the C-helix of each subunit; two syn conformations of cAMPs (syn-cAMP) bind on the surface of the C-terminal domain. With two syn-cAMP molecules bound, the D138L CAP is highly symmetrical with both subunits assuming a "closed" conformation. These differences make the hinge region of the mutant more flexible. Protease susceptibility measurements indicate that D138L is more susceptible to proteases than that of wild type (WT) CAP. The results of protein dynamic experiments (H/D exchange measurements) indicate that the structure of D138L mutant is more dynamic than that of WT CAP, which may impact the recognition of specific DNA sequences.
- Department of Chemistry and Institutes of Biomedical Science, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China.
Organizational Affiliation: