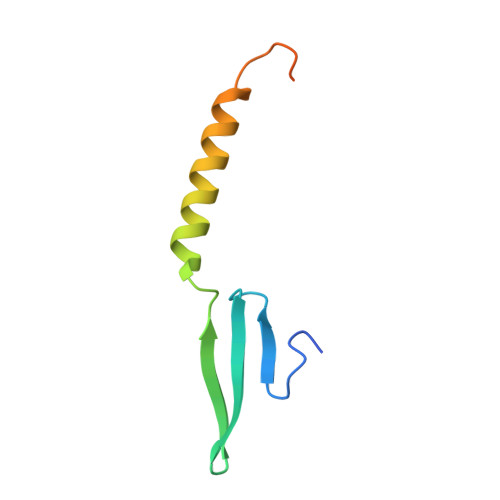
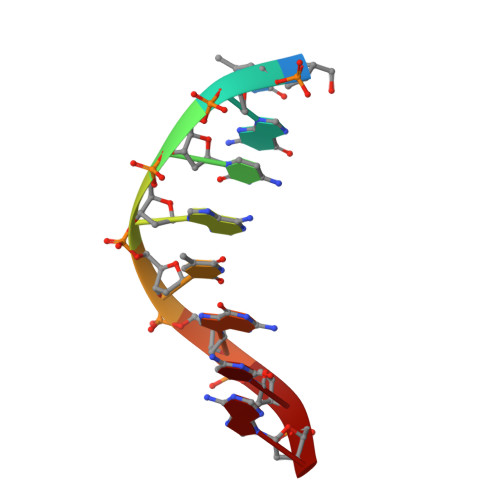
Structural Determinants of DNA Binding by a P. falciparum ApiAP2 Transcriptional Regulator.
Lindner, S.E., De Silva, E.K., Keck, J.L., Llinas, M.(2010) J Mol Biology 395: 558-567
- PubMed: 19913037
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3IGM - PubMed Abstract:
Putative transcription factors have only recently been identified in the Plasmodium spp., with the major family of regulators comprising the Apicomplexan Apetala2 (AP2) proteins. To better understand the DNA-binding mechanisms of these transcriptional regulators, we characterized the structure and in vitro function of an AP2 DNA-binding domain from a prototypical Apicomplexan AP2 protein, PF14_0633 from Plasmodium falciparum. The X-ray crystal structure of the PF14_0633 AP2 domain bound to DNA reveals a beta-sheet fold that binds the DNA major groove through base-specific and backbone contacts; a prominent alpha-helix supports the beta-sheet structure. Substitution of predicted DNA-binding residues with alanine weakened or eliminated DNA binding in solution. In contrast to plant AP2 domains, the PF14_0633 AP2 domain dimerizes upon binding to DNA through a domain-swapping mechanism in which the alpha-helices of the AP2 domains pack against the beta-sheets of the dimer mates. DNA-induced dimerization of PF14_0633 may be important for tethering two distal DNA loci together in the nucleus and/or for inducing functional rearrangements of its domains to facilitate transcriptional regulation. Consistent with a multisite binding mode, at least two copies of the consensus sequence recognized by PF14_0633 are present upstream of a previously identified group of sporozoite-stage genes. Taken together, these findings illustrate how Plasmodium has adapted the AP2 DNA-binding domain for genome-wide transcriptional regulation.
- Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, 550 Medical Sciences Center, 1300 University Avenue, Madison, WI 53706, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: