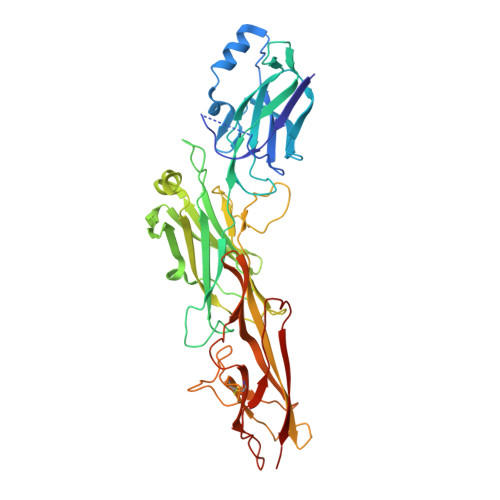
The Corynebacterium diphtheriae shaft pilin SpaA is built of tandem Ig-like modules with stabilizing isopeptide and disulfide bonds
Kang, H.J., Paterson, N.G., Gaspar, A.H., Ton-That, H., Baker, E.N.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 16967-16971
- PubMed: 19805181
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906826106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HR6, 3HTL - PubMed Abstract:
Cell-surface pili are important virulence factors that enable bacterial pathogens to adhere to specific host tissues and modulate host immune response. Relatively little is known about the structure of Gram-positive bacterial pili, which are built by the sortase-catalyzed covalent crosslinking of individual pilin proteins. Here we report the 1.6-A resolution crystal structure of the shaft pilin component SpaA from Corynebacterium diphtheriae, revealing both common and unique features. The SpaA pilin comprises 3 tandem Ig-like domains, with characteristic folds related to those typically found in non-pilus adhesins. Whereas both the middle and the C-terminal domains contain an intramolecular Lys-Asn isopeptide bond, previously detected in the shaft pilins of Streptococcus pyogenes and Bacillus cereus, the middle Ig-like domain also harbors a calcium ion, and the C-terminal domain contains a disulfide bond. By mass spectrometry, we show that the SpaA monomers are cross-linked in the assembled pili by a Lys-Thr isopeptide bond, as predicted by previous genetic studies. Together, our results reveal that despite profound dissimilarities in primary sequences, the shaft pilins of Gram-positive pathogens have strikingly similar tertiary structures, suggesting a modular backbone construction, including stabilizing intermolecular and intramolecular isopeptide bonds.
- Maurice Wilkins Centre for Molecular Biodiscovery and School of Biological Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland 1020, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: