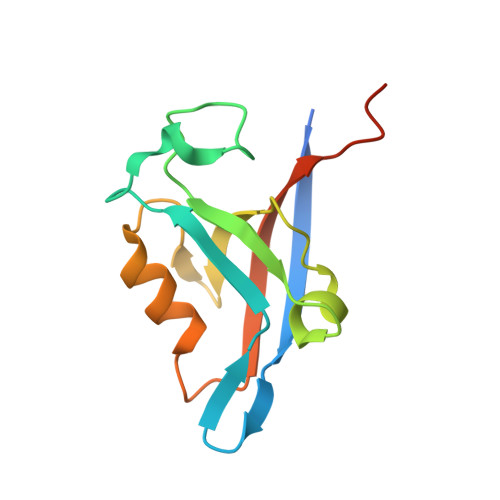
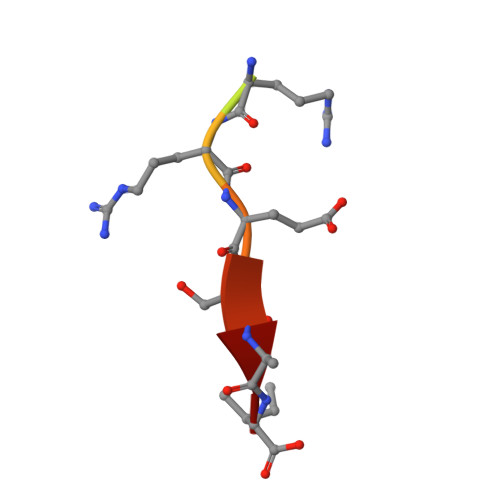
Molecular mechanism of inward rectifier potassium channel 2.3 regulation by tax-interacting protein-1
Yan, X., Zhou, H., Zhang, J., Shi, C., Xie, X., Wu, Y., Tian, C., Shen, Y., Long, J.(2009) J Mol Biology 392: 967-976
- PubMed: 19635485
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.060
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GJ9 - PubMed Abstract:
Inwardly rectifying potassium channel 2.3 (Kir2.3) is specifically targeted on the basolateral membranes of epithelial and neuronal cells, and it thus plays an important role in maintaining potassium homeostasis. Tax-interacting protein-1 (TIP-1), an atypical PDZ-domain-containing protein, binds to Kir2.3 with a high affinity, causing the intracellular accumulation of Kir2.3 in cultured epithelial cells. However, the molecular basis of the TIP-1/Kir2.3 interaction is still poorly understood. Here, we present the crystal structure of TIP-1 in complex with the C-terminal Kir2.3-peptide (residues 436-445) to reveal the molecular details of the interaction between them. Moreover, isothermal titration calorimetry experiments show that the C-terminal Kir2.3-peptide binds much more strongly to TIP-1 than to mammalian Lin-7, indicating that TIP-1 can compete with mammalian Lin-7 to uncouple Kir2.3 from its basolateral membrane anchoring complex. We further show that the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of Ser443 within the C-terminal Kir2.3 PDZ-binding motif RRESAI dynamically regulates the Kir2.3/TIP-1 association in heterologous HEK293T cells. These data suggest that TIP-1 may act as an important regulator for the endocytic pathway of Kir2.3.
- Tianjin Key Laboratory of Protein Science, College of Life Science, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China.
Organizational Affiliation: