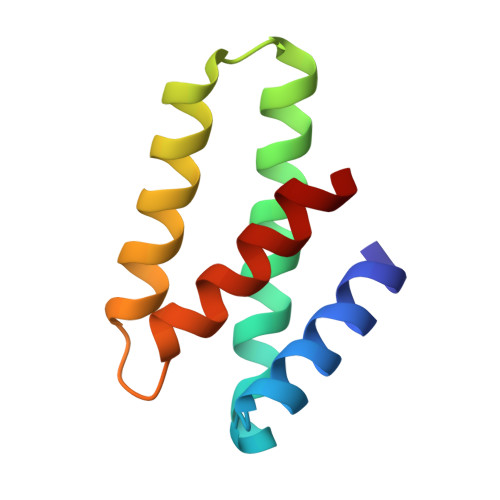
Acidianus filamentous virus 1 coat proteins display a helical fold spanning the filamentous archaeal viruses lineage
Goulet, A., Blangy, S., Redder, P., Prangishvili, D., Felisberto-Rodrigues, C., Forterre, P., Campanacci, V., Cambillau, C.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 21155-21160
- PubMed: 19934032
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909893106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FBL, 3FBZ - PubMed Abstract:
Acidianus filamentous virus 1 (AFV1), a member of the Lipothrixviridae family, infects the hyperthermophilic, acidophilic crenarchaeaon Acidianus hospitalis. The virion, covered with a lipidic outer shell, is 9,100-A long and contains a 20.8-kb linear dsDNA genome. We have identified the two major coat proteins of the virion (MCPs; 132 and 140 amino acids). They bind DNA and form filaments when incubated with linear dsDNA. A C-terminal domain is identified in their crystal structure with a four-helix-bundle fold. In the topological model of the virion filament core, the genomic dsDNA superhelix wraps around the AFV1-132 basic protein, and the AFV1-140 basic N terminus binds genomic DNA, while its lipophilic C-terminal domain is imbedded in the lipidic outer shell. The four-helix bundle fold of the MCPs from AFV1 is identical to that of the coat protein (CP) of Sulfolobus islandicus rod-shaped virus (SIRV), a member of the Rudiviridae family. Despite low sequence identity between these proteins, their high degree of structural similarity suggests that they could have derived from a common ancestor and could thus define an yet undescribed viral lineage.
- Architecture et Fonction des Macromolécules Biologiques, Centre national de la Recherche Scientifique and Universités Aix-Marseille I & II, Architecture et Fonction des Macromolécules Biologiques, Unité Mixte de Recherche 6098, Case 932, 163 avenue de Luminy, 13288 Marseille Cedex 9, France.
Organizational Affiliation: