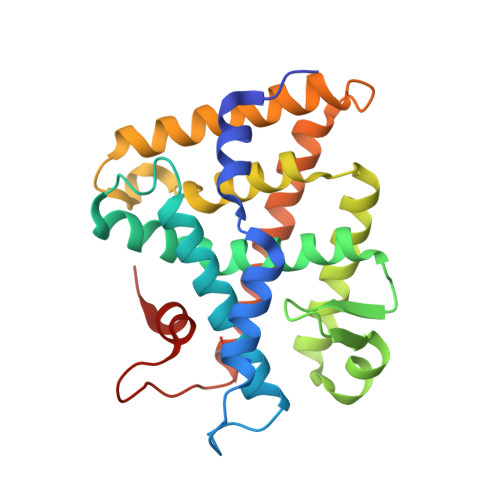
Structure of SF-1 bound by different phospholipids: evidence for regulatory ligands.
Sablin, E.P., Blind, R.D., Krylova, I.N., Ingraham, J.G., Cai, F., Williams, J.D., Fletterick, R.J., Ingraham, H.A.(2009) Mol Endocrinol 23: 25-34
- PubMed: 18988706
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0508
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3F7D - PubMed Abstract:
Despite the fact that many nuclear receptors are ligand dependent, the existence of obligate regulatory ligands is debated for some receptors, including steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1). Although fortuitously bound bacterial phospholipids were discovered in the structures of the SF-1 ligand-binding domain (LBD), these lipids might serve merely as structural ligands. Thus, we examined whether exogenously added phospholipids would exchange for these bacterial lipids and bind to SF-1. Here, we report the first crystal structure of the SF-1 LBD bound by the exchanged phosphatidylcholine. Although the bound phosphatidylcholine phospholipid mimics the conformation of bound bacterial phosphoplipids, two surface loops, L2-3 and L11-12, surrounding the entrance to the pocket vary significantly between different SF-1 LBD structures. Based on this observation, we hypothesized that a bound ligand might control the conformations of loops L2-3 and L11-12, and that conserved residues in these dynamic loops could influence ligand binding and the receptor function. Consistent with this hypothesis, impaired phospholipid exchange and diminished transcriptional activity were observed for loop L11-12 SF-1 mutants and for the loop L2-3 human mutant R255L. The endocrine disease associated with this L2-3 mutation coupled with our cellular and biochemical data suggest that critical residues at the mouth of the ligand-binding pocket have evolved for efficient binding of phospholipid ligands and for achieving optimal SF-1 activity.
- Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of California, San Francisco, California 94143, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: