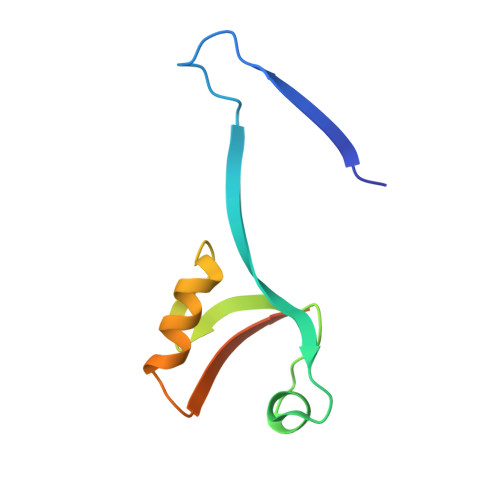
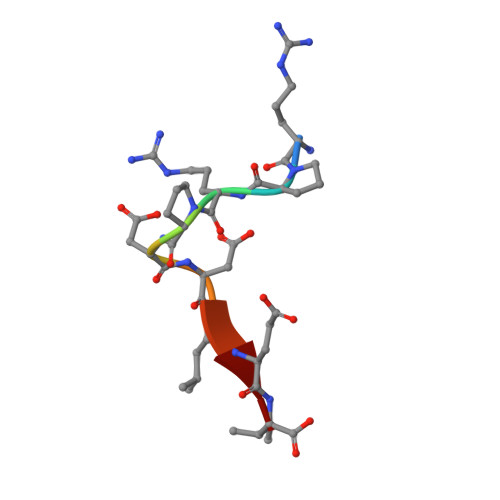
Domain-swapped dimerization of ZO-1 PDZ2 generates specific and regulatory connexin43-binding sites
Chen, J., Pan, L., Wei, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, M.(2008) EMBO J 27: 2113-2123
- PubMed: 18636092
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.138
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CYY - PubMed Abstract:
PDZ domain scaffold proteins are capable of assembling macromolecular protein complexes in diverse cellular processes through PDZ-mediated binding to a short peptide fragment at the carboxyl tail of target proteins. How each PDZ domain specifically recognizes its target protein(s) remains a major conceptual question, as at least a few out of the several hundred PDZ domains in each eukaryotic genome share overlapping binding properties with any given target protein. Here, we show that the domain-swapped dimerization of zonula occludens-1 PDZ2 generates a distinct interface that functions together with the well-separated canonical carboxyl tail-binding pocket in each PDZ unit in binding to connexin43 (Cx43). We further demonstrate that the charge-charge interaction network formed by residues in the PDZ dimer interface and upstream residues of the Cx43 peptide not only provides the unprecedented interaction specificity for the complex but may also function as a phosphorylation-mediated regulatory switch for the dynamics of the Cx43 gap junctions. Finally, we provide evidence that such domain-swapped dimer assembly also occurs in other PDZ domain scaffold proteins. Therefore, our findings present a new paradigm for understanding how some PDZ domain proteins specifically bind to and regulate the functions of their target proteins.
- Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Neuroscience Center, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong.
Organizational Affiliation: