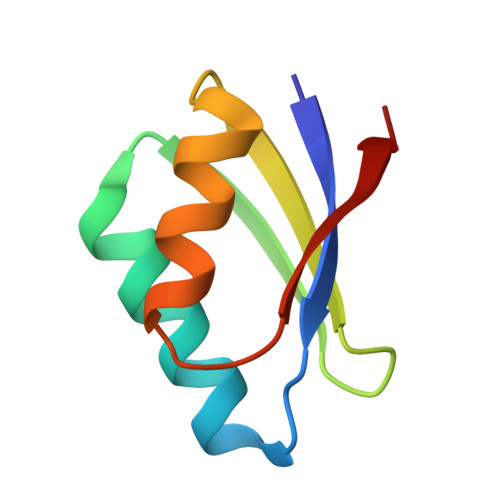
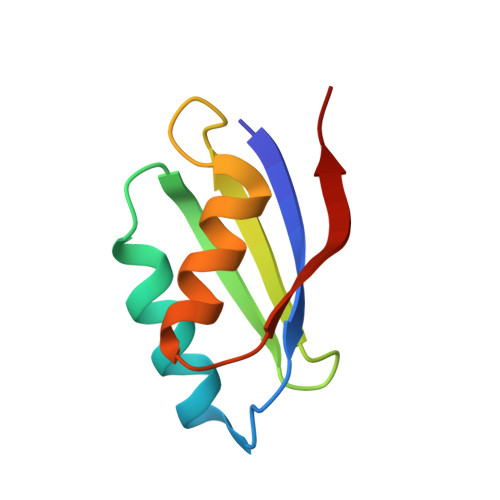
Copper(I)-mediated protein-protein interactions result from suboptimal interaction surfaces.
Banci, L., Bertini, I., Calderone, V., Della-Malva, N., Felli, I.C., Neri, S., Pavelkova, A., Rosato, A.(2009) Biochem J 422: 37-42
- PubMed: 19453293
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20090422
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CJK - PubMed Abstract:
The homoeostasis of metal ions in cells is the result of the contribution of several cellular pathways that involve transient, often weak, protein-protein interactions. Metal transfer typically implies the formation of adducts where the metal itself acts as a bridge between proteins, by co-ordinating residues of both interacting partners. In the present study we address the interaction between the human copper(I)-chaperone HAH1 (human ATX1 homologue) and a metal-binding domain in one of its partners, namely the P-type copper-transporting ATPase, ATP7A (ATPase, Cu+ transporting, alpha polypeptide). The adduct was structurally characterized in solution, in the presence of copper(I), and through X-ray crystallography, upon replacing copper(I) with cadmium(II). Further insight was obtained through molecular modelling techniques and site-directed mutagenesis. It was found that the interaction involves a relatively small interface (less than 1000 A(2), 1 A=0.1 nm) with a low fraction of non-polar atoms. These observations provide a possible explanation for the low affinity of the two apoproteins. It appears that electrostatics is important in selecting which domain of the ATPase is able to form detectable amounts of the metal-mediated adduct with HAH1.
- Magnetic Resonance Center (CERM), University of Florence, Sesto Fiorentino, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: