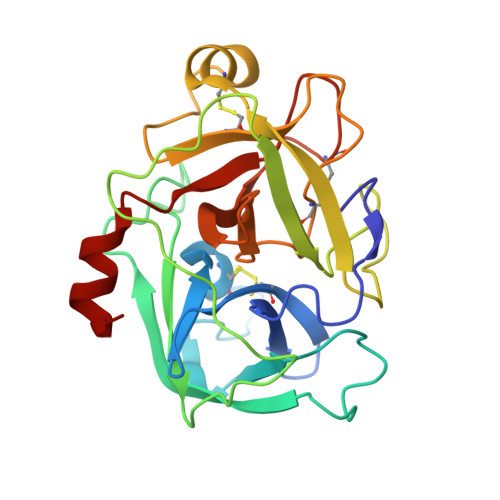
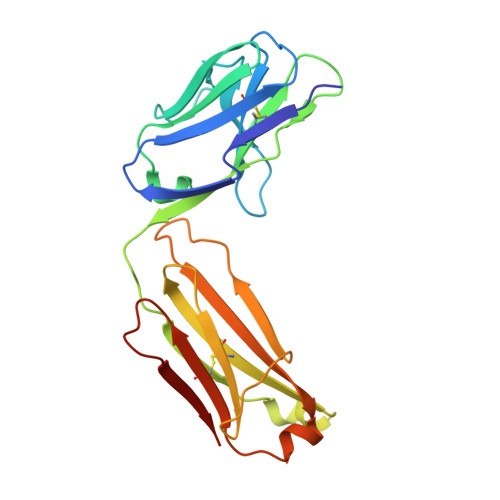
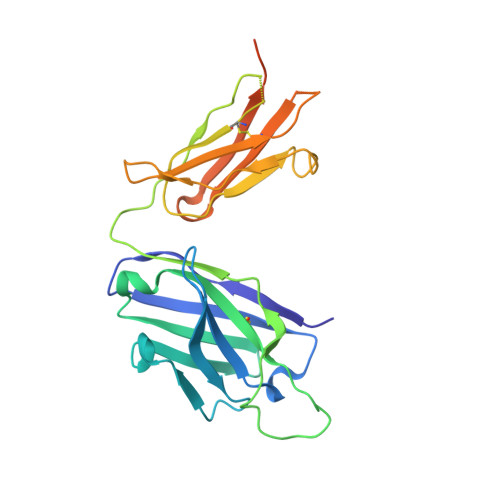
Structure of an Fab-protease complex reveals a highly specific non-canonical mechanism of inhibition
Farady, C.J., Egea, P.F., Schneider, E.L., Darragh, M.R., Craik, C.S.(2008) J Mol Biology 380: 351-360
- PubMed: 18514224
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BN9 - PubMed Abstract:
The vast majority of protein protease inhibitors bind their targets in a substrate-like manner. This is a robust and efficient mechanism of inhibition but, due to the highly conserved architecture of protease active sites, these inhibitors often exhibit promiscuity. Inhibitors that show strict specificity for one protease usually achieve this selectivity by combining substrate-like binding in the active site with exosite binding on the protease surface. The development of new, specific inhibitors can be aided greatly by binding to non-conserved regions of proteases if potency can be maintained. Due to their ability to bind specifically to nearly any antigen, antibodies provide an excellent scaffold for creating inhibitors targeted to a single member of a family of highly homologous enzymes. The 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of an Fab antibody inhibitor in complex with the serine protease membrane-type serine protease 1 (MT-SP1/matriptase) reveals the molecular basis of its picomolar potency and specificity. The inhibitor has a distinct mechanism of inhibition; it gains potency and specificity through interactions with the protease surface loops, and inhibits by binding in the active site in a catalytically non-competent manner. In contrast to most naturally occurring protease inhibitors, which have diverse structures but converge to a similar inhibitory archetype, antibody inhibitors provide an opportunity to develop divergent mechanisms of inhibition from a single scaffold.
- Graduate Group in Biophysics, University of California, San Francisco, 600 16th St. Genentech Hall, San Francisco, CA 94143-2240, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: