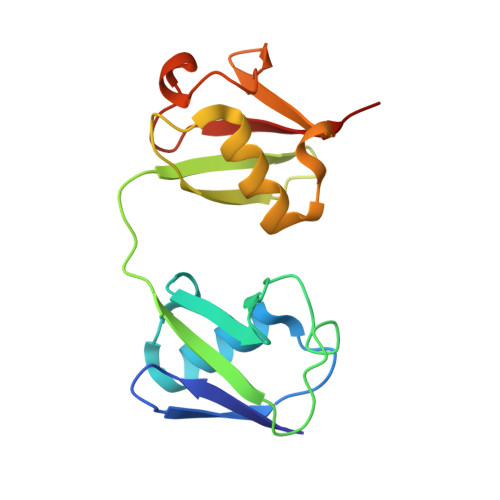
Structure of a compact conformation of linear diubiquitin
Rohaim, A., Kawasaki, M., Kato, R., Dikic, I., Wakatsuki, S.(2012) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 68: 102-108
- PubMed: 22281738
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444911051195
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AXC - PubMed Abstract:
Post-translational modifications involving ubiquitin regulate a wide range of biological processes including protein degradation, responses to DNA damage and immune signalling. Ubiquitin polymerizes into chains which may contain eight different linkage types; the ubiquitin C-terminal glycine can link to one of the seven lysine residues or the N-terminal amino group of methionine in the distal ubiquitin molecule. The latter head-to-tail linkage type, referred to as a linear ubiquitin chain, is involved in NF-κB activation through specific interactions with NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO). Here, a crystal structure of linear diubiquitin at a resolution of 2.2 Å is reported. Although the two ubiquitin moieties do not interact with each other directly, the overall structure adopts a compact but not completely closed conformation with a few intermoiety contacts. This structure differs from the previously reported extended conformation, which resembles Lys63-linked diubiquitin, suggesting that the linear polyubiquitin chain is intrinsically flexible and can adopt multiple conformations.
- Structural Biology Research Center, Photon Factory, Institute of Materials Structure Science, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: