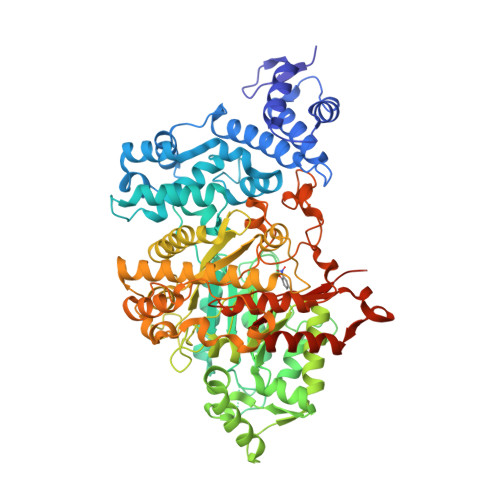
Site-Specific Incorporation of 3-Nitrotyrosine as a Probe of Pk(A) Perturbation of Redox-Active Tyrosines in Ribonucleotide Reductase.
Yokoyama, K., Uhlin, U., Stubbe, J.(2010) J Am Chem Soc 132: 8385
- PubMed: 20518462
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja101097p
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2X0X, 2XAK, 2XAP, 2XAV, 2XAW, 2XAX, 2XAY, 2XAZ - PubMed Abstract:
E. coli ribonucleotide reductase catalyzes the reduction of nucleoside 5'-diphosphates into 2'-deoxynucleotides and is composed of two subunits: alpha2 and beta2. During turnover, a stable tyrosyl radical (Y*) at Y(122)-beta2 reversibly oxidizes C(439) in the active site of alpha2. This radical propagation step is proposed to occur over 35 A, to use specific redox-active tyrosines (Y(122) and Y(356) in beta2, Y(731) and Y(730) in alpha2), and to involve proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET). 3-Nitrotyrosine (NO(2)Y, pK(a) 7.1) has been incorporated in place of Y(122), Y(731), and Y(730) to probe how the protein environment perturbs each pK(a) in the presence of the second subunit, substrate (S), and allosteric effector (E). The activity of each mutant is <4 x 10(-3) that of the wild-type (wt) subunit. The [NO(2)Y(730)]-alpha2 and [NO(2)Y(731)]-alpha2 each exhibit a pK(a) of 7.8-8.0 with E and E/beta2. The pK(a) of [NO(2)Y(730)]-alpha2 is elevated to 8.2-8.3 in the S/E/beta2 complex, whereas no further perturbation is observed for [NO(2)Y(731)]-alpha2. Mutations in pathway residues adjacent to the NO(2)Y that disrupt H-bonding minimally perturb its pK(a). The pK(a) of NO(2)Y(122)-beta2 alone or with alpha2/S/E is >9.6. X-ray crystal structures have been obtained for all [NO(2)Y]-alpha2 mutants (2.1-3.1 A resolution), which show minimal structural perturbation compared to wt-alpha2. Together with the pK(a) of the previously reported NO(2)Y(356)-beta2 (7.5 in the alpha2/S/E complex; Yee, C. et al. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14541-14552), these studies provide a picture of the protein environment of the ground state at each Y in the PCET pathway, and are the starting point for understanding differences in PCET mechanisms at each residue in the pathway.
- Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139-4307, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: