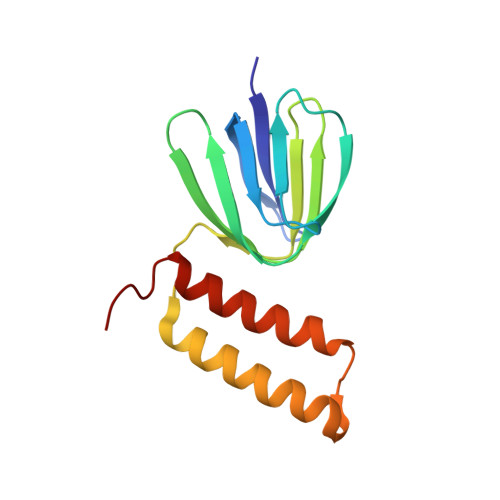
Structural and functional analysis of the intrinsic inhibitor subunit epsilon of F1-ATPase from photosynthetic organisms.
Yagi, H., Konno, H., Murakami-Fuse, T., Isu, A., Oroguchi, T., Akutsu, H., Ikeguchi, M., Hisabori, T.(2010) Biochem J 425: 85-94
- PubMed: 19785575
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20091247
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RQ6, 2RQ7 - PubMed Abstract:
The epsilon subunit, a small subunit located in the F1 domain of ATP synthase and comprising two distinct domains, an N-terminal beta-sandwich structure and a C-terminal alpha-helical region, serves as an intrinsic inhibitor of ATP hydrolysis activity. This inhibitory function is especially important in photosynthetic organisms as the enzyme cannot synthesize ATP in the dark, but may catalyse futile ATP hydrolysis reactions. To understand the structure-function relationship of this subunit in F1 from photosynthetic organisms, we solved the NMR structure of the epsilon subunit of ATP synthase obtained from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1, and examined the flexibility of the C-terminal domains using molecular dynamics simulations. In addition, we revealed the significance of the C-terminal alpha-helical region of the epsilon subunit in determining the binding affinity to the complex based on the assessment of the inhibition of ATPase activity by the cyanobacterial epsilon subunit and the chimaeric subunits composed of the N-terminal domain from the cyanobacterium and the C-terminal domain from spinach. The differences observed in the structural and biochemical properties of chloroplast and bacterial epsilon subunits explains the distinctive characteristics of the epsilon subunits in the ATPase complex of the photosynthetic organism.
- Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, 3-2 Yamadaoka, Suita 565-0871, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: