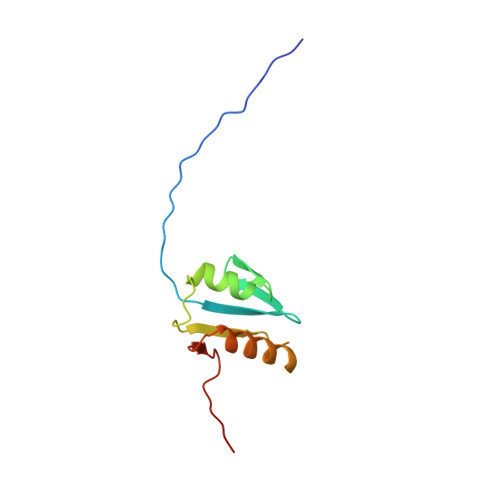
The solution structure of the periplasmic domain of the TonB system ExbD protein reveals an unexpected structural homology with siderophore-binding proteins.
Garcia-Herrero, A., Peacock, R.S., Howard, S.P., Vogel, H.J.(2007) Mol Microbiol 66: 872-889
- PubMed: 17927700
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05957.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PFU - PubMed Abstract:
The transport of iron complexes through outer membrane transporters from Gram-negative bacteria is highly dependent on the TonB system. Together, the three components of the system, TonB, ExbB and ExbD, energize the transport of iron complexes through the outer membrane by utilizing the proton motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane. The three-dimensional (3D) structure of the periplasmic domain of TonB has previously been determined. However, no detailed structural information for the other two components of the TonB system is currently available and their role in the iron-uptake process is not yet clearly understood. ExbD from Escherichia coli contains 141 residues distributed in three domains: a small N-terminal cytoplasmic region, a single transmembrane helix and a C-terminal periplasmic domain. Here we describe the first well-defined solution structure of the periplasmic domain of ExbD (residues 44-141) solved by multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The monomeric structure presents three clearly distinct regions: an N-terminal flexible tail (residues 44-63), a well-defined folded region (residues 64-133) followed by a small C-terminal flexible region (residues 134-141). The folded region is formed by two alpha-helices that are located on one side of a single beta-sheet. The central beta-sheet is composed of five beta-strands, with a mixed parallel and antiparallel arrangement. Unexpectedly, this fold closely resembles that found in the C-terminal lobe of the siderophore-binding proteins FhuD and CeuE. The ExbD periplasmic domain has a strong tendency to aggregate in vitro and 3D-TROSY (transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy) NMR experiments of the deuterated protein indicate that the multimeric protein has nearly identical secondary structure to that of the monomeric form. Chemical shift perturbation studies suggest that the Glu-Pro region (residues 70-83) of TonB can bind weakly to the surface and the flexible C-terminal region of ExbD. At the same time the Lys-Pro region (residues 84-102) and the folded C-terminal domain (residues 150-239) of TonB do not show significant binding to ExbD, suggesting that the main interactions forming the TonB complex occur in the cytoplasmic membrane.
- Structural Biology Research Group, Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary, Alberta, T2N 1 N4 Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: