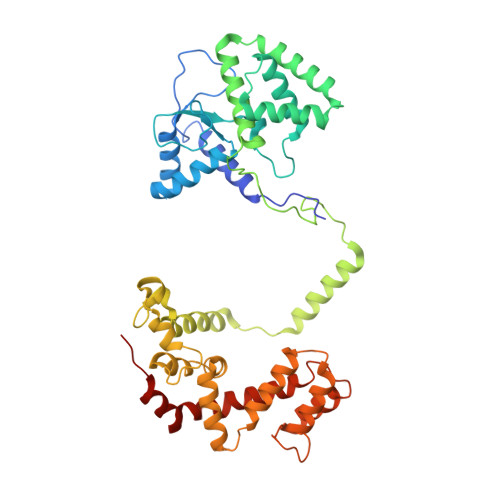
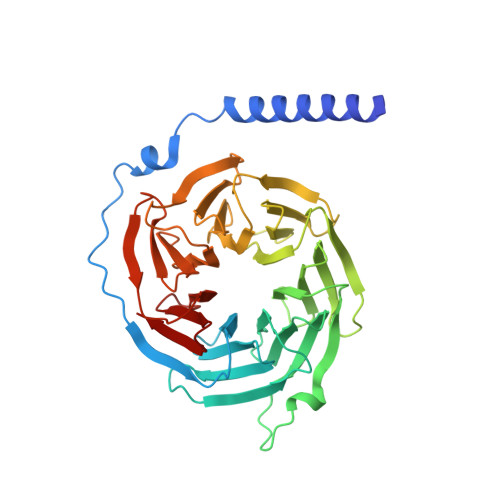
Crystal structure of the multifunctional Gbeta5-RGS9 complex.
Cheever, M.L., Snyder, J.T., Gershburg, S., Siderovski, D.P., Harden, T.K., Sondek, J.(2008) Nat Struct Mol Biol 15: 155-162
- PubMed: 18204463
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1377
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PBI - PubMed Abstract:
Regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins enhance the intrinsic GTPase activity of G protein alpha (Galpha) subunits and are vital for proper signaling kinetics downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). R7 subfamily RGS proteins specifically and obligately dimerize with the atypical G protein beta5 (Gbeta5) subunit through an internal G protein gamma (Ggamma)-subunit-like (GGL) domain. Here we present the 1.95-A crystal structure of the Gbeta5-RGS9 complex, which is essential for normal visual and neuronal signal transduction. This structure reveals a canonical RGS domain that is functionally integrated within a molecular complex that is poised for integration of multiple steps during G-protein activation and deactivation.
- Department of Pharmacology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Campus Box 7365, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599-7365, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: