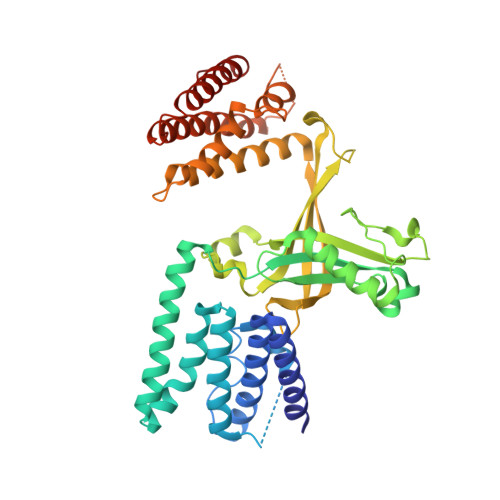
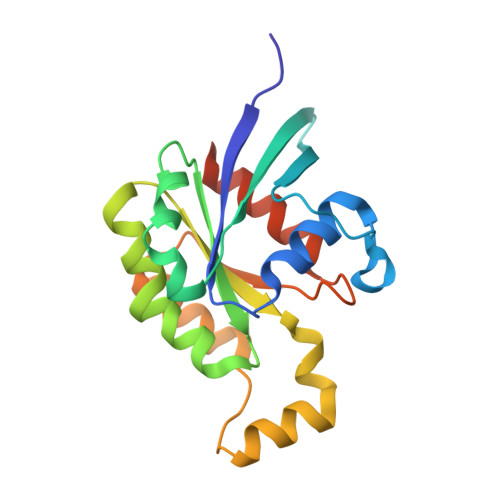
Activation of Rho Gtpases by Dock Exchange Factors is Mediated by a Nucleotide Sensor.
Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Roe, S.M., Marshall, C.J., Barford, D.(2009) Science 325: 1398
- PubMed: 19745154
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1174468
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WM9, 2WMN, 2WMO - PubMed Abstract:
Activation of Rho guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) to the guanine triphosphate (GTP)-bound state is a critical event in their regulation of the cytoskeleton and cell signaling. Members of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are important activators of Rho GTPases, but the mechanism of activation by their catalytic DHR2 domain is unknown. Through structural analysis of DOCK9-Cdc42 complexes, we identify a nucleotide sensor within the alpha10 helix of the DHR2 domain that contributes to release of guanine diphosphate (GDP) and then to discharge of the activated GTP-bound Cdc42. Magnesium exclusion, a critical factor in promoting GDP release, is mediated by a conserved valine residue within this sensor, whereas binding of GTP-Mg2+ to the nucleotide-free complex results in magnesium-inducing displacement of the sensor to stimulate discharge of Cdc42-GTP. These studies identify an unusual mechanism of GDP release and define the complete GEF catalytic cycle from GDP dissociation followed by GTP binding and discharge of the activated GTPase.
- Section of Structural Biology, Institute of Cancer Research, Chester Beatty Laboratories, 237 Fulham Road, London SW3 6JB, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: