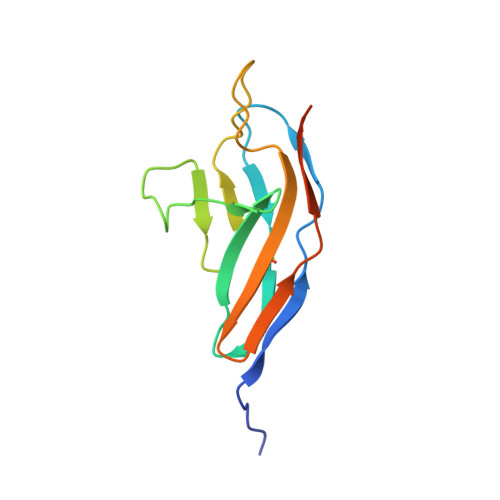
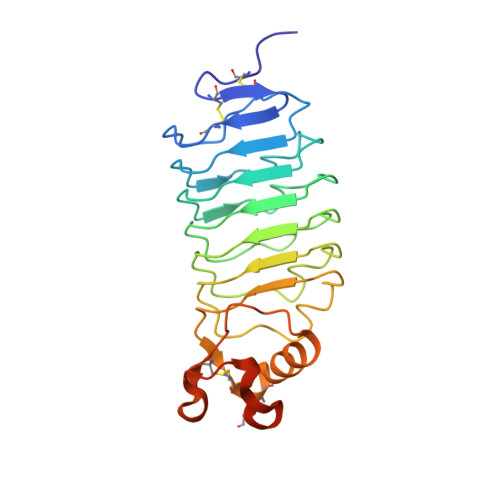
Structural Insights Into the Slit-Robo Complex.
Morlot, C., Thielens, N.M., Ravelli, R.B., Hemrika, W., Romijn, R.A., Gros, P., Cusack, S., Mccarthy, A.A.(2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 14923
- PubMed: 17848514
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705310104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V9Q, 2V9R, 2V9S, 2V9T - PubMed Abstract:
Slits are large multidomain leucine-rich repeat (LRR)-containing proteins that provide crucial guidance cues in neuronal and vascular development. More recently, Slits have been implicated in heart morphogenesis, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. Slits are ligands for the Robo (Roundabout) receptors, which belong to the Ig superfamily of transmembrane signaling molecules. The Slit-Robo interaction is mediated by the second LRR domain of Slit and the two N-terminal Ig domains of Robo, but the molecular details of this interaction and how it induces signaling remain unclear. Here we describe the crystal structures of the second LRR domain of human Slit2 (Slit2 D2), the first two Ig domains of its receptor Robo1 (Ig1-2), and the minimal complex between these proteins (Slit2 D2-Robo1 Ig1). Slit2 D2 binds with its concave surface to the side of Ig1 with electrostatic and hydrophobic contact regions mediated by residues that are conserved in other family members. Surface plasmon resonance experiments and a mutational analysis of the interface confirm that Ig1 is the primary domain for binding Slit2. These structures provide molecular insight into Slit-Robo complex formation and will be important for the development of novel cancer therapeutics.
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory, 6 Rue Jules Horowitz, BP 181, 38042 Grenoble, France.
Organizational Affiliation: