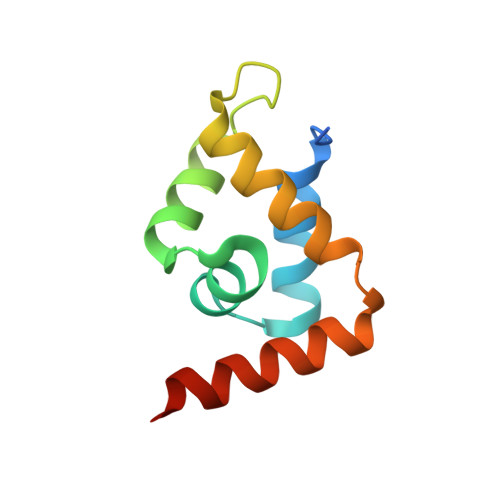
Structural basis for recognition of the matrix attachment region of DNA by transcription factor SATB1.
Yamasaki, K., Akiba, T., Yamasaki, T., Harata, K.(2007) Nucleic Acids Res 35: 5073-5084
- PubMed: 17652321
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm504
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2O49, 2O4A - PubMed Abstract:
Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 (SATB1) regulates gene expression essential in immune T-cell maturation and switching of fetal globin species, by binding to matrix attachment regions (MARs) of DNA and inducing a local chromatin remodeling. Previously we have revealed a five-helix structure of the N-terminal CUT domain, which is essentially the folded region in the MAR-binding domain, of human SATB1 by NMR. Here we determined crystal structure of the complex of the CUT domain and a MAR DNA, in which the third helix of the CUT domain deeply enters the major groove of DNA in the B-form. Bases of 5'-CTAATA-3' sequence are contacted by this helix, through direct and water-mediated hydrogen bonds and apolar and van der Waals contacts. Mutations at conserved base-contacting residues, Gln402 and Gly403, reduced the DNA-binding activity, which confirmed the importance of the observed interactions involving these residues. A significant number of equivalent contacts are observed also for typically four-helix POU-specific domains of POU-homologous proteins, indicating that these domains share a common framework of the DNA-binding mode, recognizing partially similar DNA sequences.
- Age Dimension Research Center, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba, Japan. yamasaki@aist.go.jp
Organizational Affiliation: