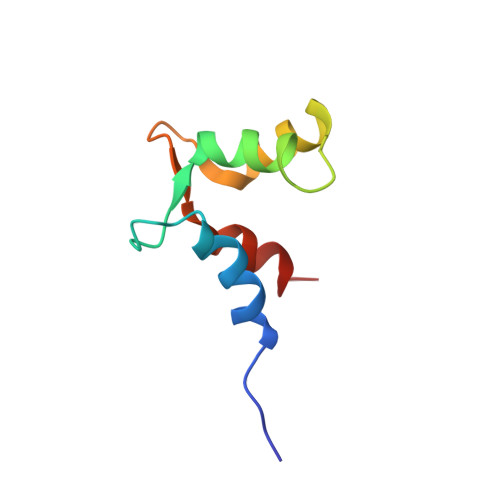
PEP-19 modulates calcium binding to calmodulin by electrostatic steering.
Wang, X., Putkey, J.A.(2016) Nat Commun 7: 13583-13583
- PubMed: 27876793
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13583
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N77 - PubMed Abstract:
PEP-19 is a small protein that increases the rates of Ca 2+ binding to the C-domain of calmodulin (CaM) by an unknown mechanism. Although an IQ motif promotes binding to CaM, an acidic sequence in PEP-19 is required to modulate Ca 2+ binding and to sensitize HeLa cells to ATP-induced Ca 2+ release. Here, we report the NMR solution structure of a complex between PEP-19 and the C-domain of apo CaM. The acidic sequence of PEP-19 associates between helices E and F of CaM via hydrophobic interactions. This allows the acidic side chains in PEP-19 to extend toward the solvent and form a negatively charged surface that resembles a catcher's mitt near Ca 2+ binding loop III of CaM. The topology and gradients of negative electrostatic surface potential support a mechanism by which PEP-19 increases the rate of Ca 2+ binding to the C-domain of CaM by 'catching' and electrostatically steering Ca 2+ to site III.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, McGovern Medical at UTHealth, 6431 Fannin, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: