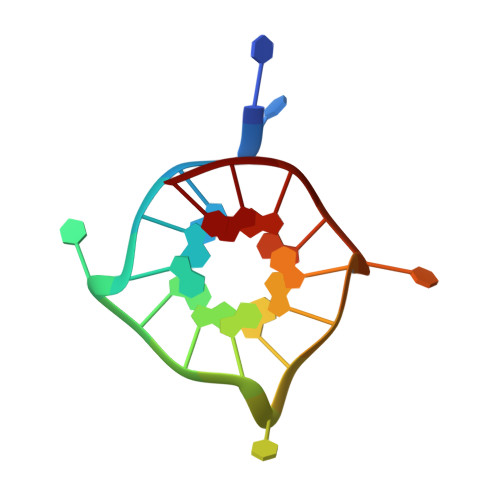
Insights into G-quadruplex specific recognition by the DEAH-box helicase RHAU: Solution structure of a peptide-quadruplex complex.
Heddi, B., Cheong, V.V., Martadinata, H., Phan, A.T.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 9608-9613
- PubMed: 26195789
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422605112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N16, 2N21 - PubMed Abstract:
Four-stranded nucleic acid structures called G-quadruplexes have been associated with important cellular processes, which should require G-quadruplex-protein interaction. However, the structural basis for specific G-quadruplex recognition by proteins has not been understood. The DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box RNA helicase associated with AU-rich element (RHAU) (also named DHX36 or G4R1) specifically binds to and resolves parallel-stranded G-quadruplexes. Here we identified an 18-amino acid G-quadruplex-binding domain of RHAU and determined the structure of this peptide bound to a parallel DNA G-quadruplex. Our structure explains how RHAU specifically recognizes parallel G-quadruplexes. The peptide covers a terminal guanine base tetrad (G-tetrad), and clamps the G-quadruplex using three-anchor-point electrostatic interactions between three positively charged amino acids and negatively charged phosphate groups. This binding mode is strikingly similar to that of most ligands selected for specific G-quadruplex targeting. Binding to an exposed G-tetrad represents a simple and efficient way to specifically target G-quadruplex structures.
- School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371.
Organizational Affiliation: